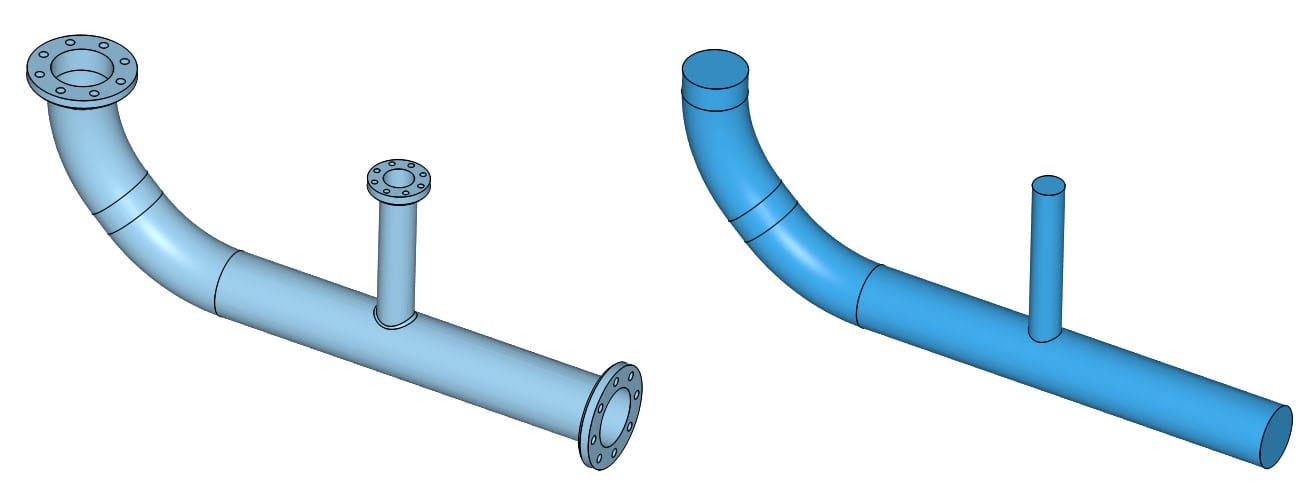
The simulation domain for a fluid dynamics simulation is the region occupied by the fluid (gas or liquid). However, in many cases, the CAD model will not contain the fluid volume by default. In such cases you can extract the fluid region, using the Flow volume extraction feature under the CAD mode. Afterwards, we need to delete the solid body.
We call this process, Fluid Volume Extraction.
In order to illustrate the problem further, see the basic use case of a flow simulation through a pipe below.
There are two flow volume extraction modes available within SimScale:
- Internal Flow Volume
- External Flow Volume
Depending on your geometry, you may use one of two modes to extract the fluid volume. Find examples below about the application for each of the types.
1. Internal Flow Volume
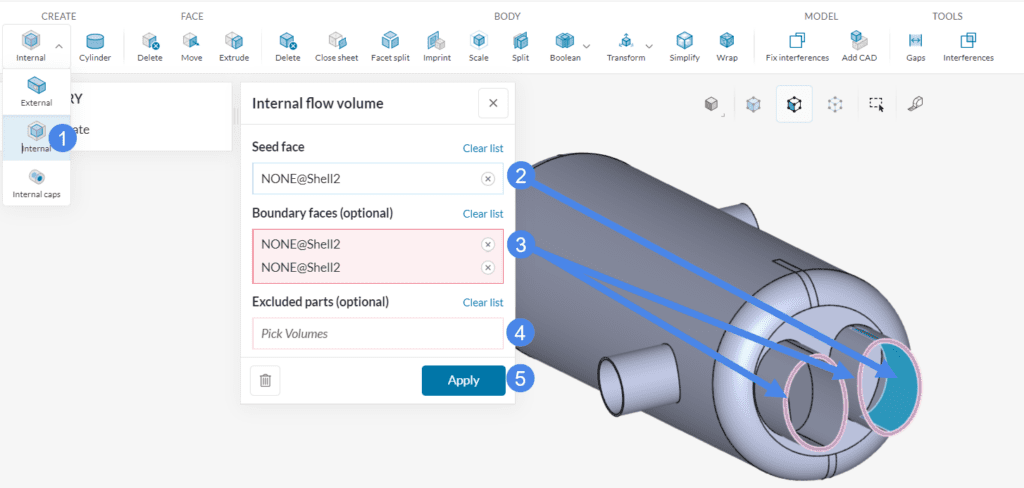
This operation generates an internal flow volume. For instance, the example below shows how to generate the internal flow volume of a heat exchanger. The heat exchanger has two openings for each fluid. Extract one of the flow volumes as follows:
- Select ‘Internal‘.
- Select one internal Seed face (blue).
- Select the Boundary faces that lie between the external environment and the internal (highlighted in pink).
- In case there are cell zones in your model, assign them to Excluded parts. If not, leave it empty.
- Hit ‘Apply’ to run the operation.
This will result in a geometry that contains both the fluid volume as well as the outer wall geometry, as two separate parts. However, for a simple fluid flow simulation, you need only a single fluid volume. Keep the outer wall geometry (solid body) only in case of a conjugate heat transfer simulation in which the transfer of heat between the solid parts and the fluid domain needs to be simulated. If you are going to perform a single region analysis like incompressible, compressible, or convective heat transfer, you need to delete the solid body as follows:
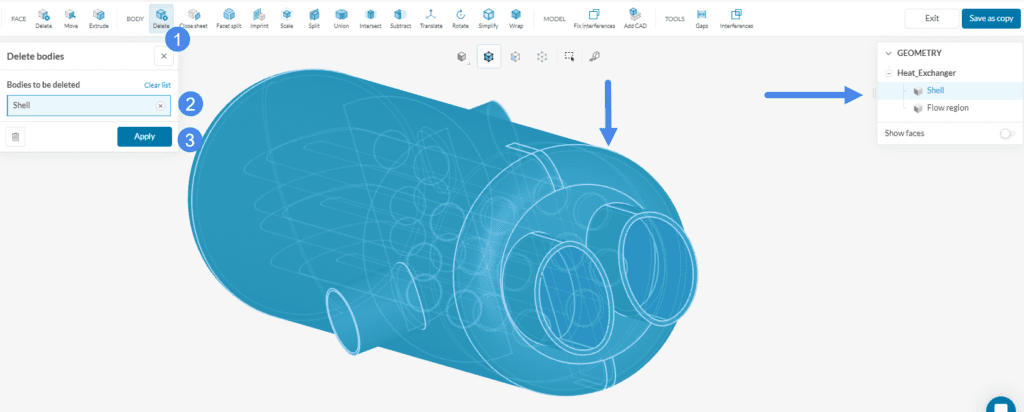
- Choose the ‘Delete’ operation under BODY.
- Pick the solid volume that needs to be removed. In this example, it is the Shell.
- Hit ‘Apply’.
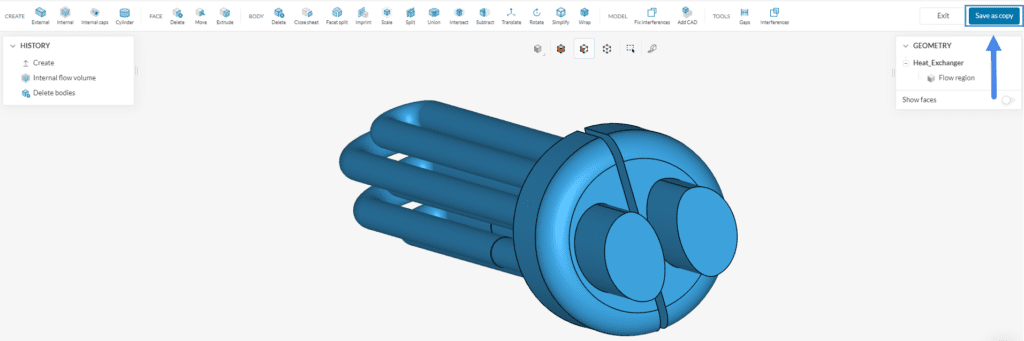
After all the operations are concluded exit CAD mode by clicking on ‘Save as copy’. This will direct you to the Workbench.
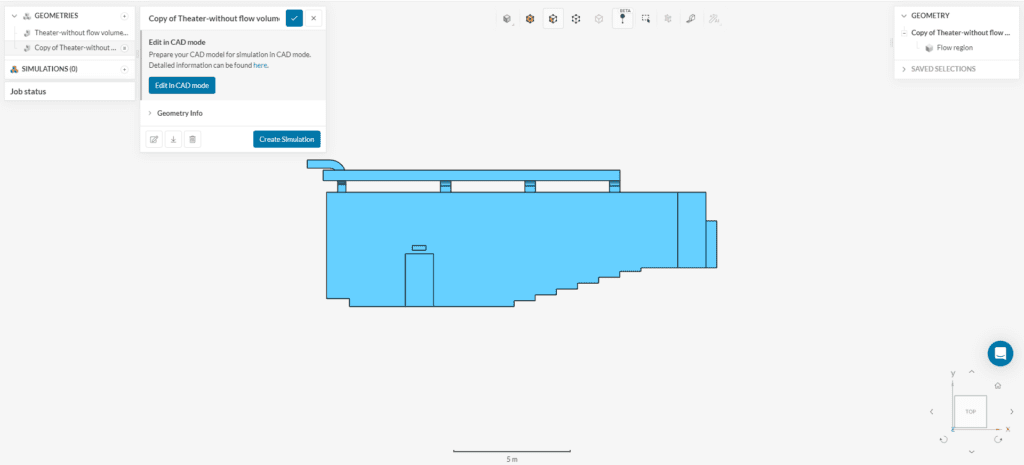
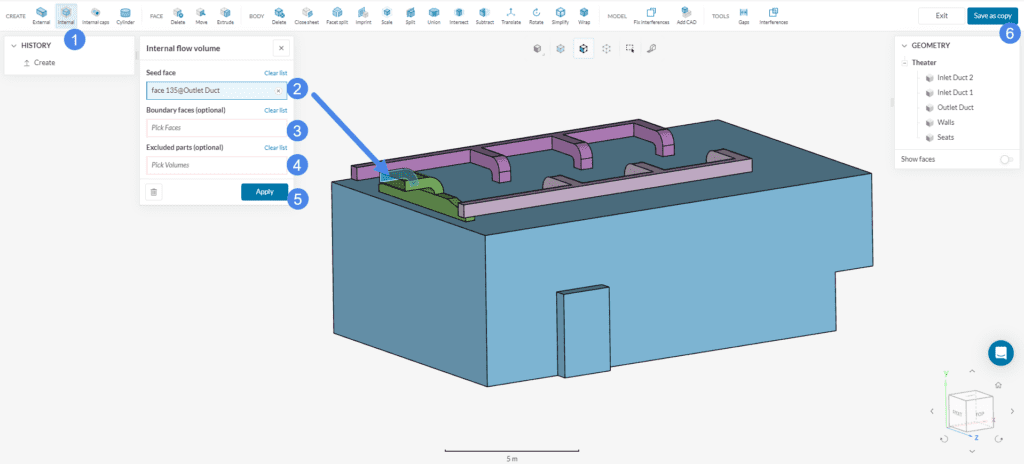
The model might be completely enclosed, in other words without any openings. In the following figure, you see the walls and ducting of a theatre model which has no openings. If this is the case, firstly, use the select other feature to select an internal face, which is in contact with the fluid region, as seed face. Then, extract the internal flow volume to be able to perform an HVAC simulation, as follows:
- Select ‘Internal‘.
- Select one internal Seed face (blue)
- Leave the Boundary faces empty.
- In case there are cell zones in your model, assign them to Excluded parts. If not, leave it empty.
- Hit ‘Apply’ to run the operation.
After the flow volume extraction, you can delete the solid bodies to be able to perform a convective heat transfer analysis. Finally, export the model to the Workbench. The new CAD model name starts with “Copy of…” and continues with the original CAD name.
2. External Flow Volume
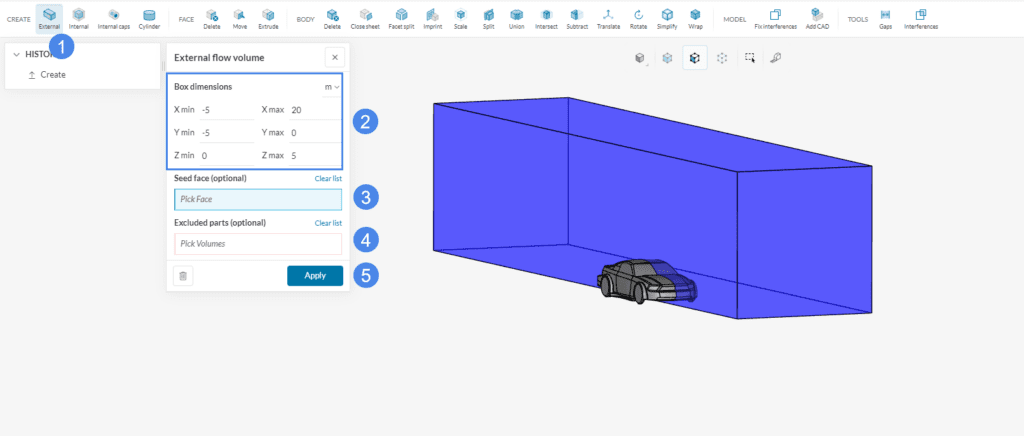
Above all, this option is often suitable for external flow problems. First, you need to size the external flow volume, and then run the operation. For instance, the example below shows how to generate a half-symmetrical air domain for a vehicle CAD geometry.
- Select ‘External‘.
- Define the External flow volume size by adjusting the minimum and maximum coordinates of the flow domain box.
- If your model has internal voids, define the ‘seed face’ to be able to differentiate the voids from the external flow volume. Visit this article to learn more about the seed face.
- In case there are cell zones in your model, assign them to Excluded parts. If not, leave it empty.
- Hit ‘Apply’ to run the operation.
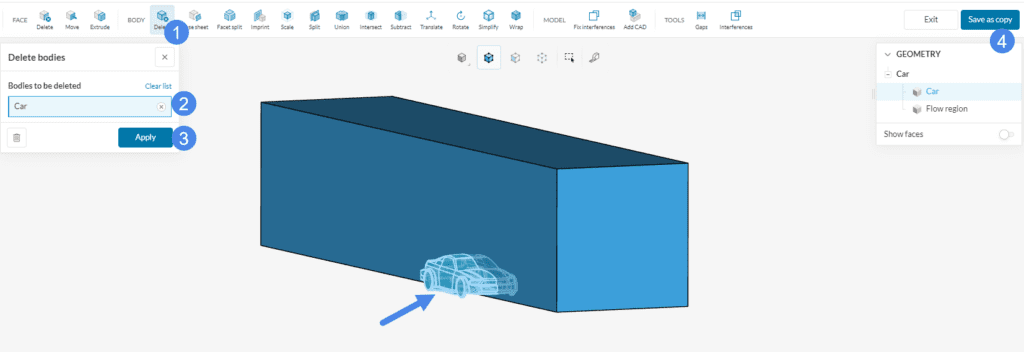
In addition, delete the solid parts to be able to use the model in an analysis type that requires a single fluid region:
- Pick the ‘Delete’ operation under BODY
- Select the aircraft body.
- Hit ‘Apply’.
- Click ‘Save as copy’ to export the new CAD version to your Workbench.
Before creating the external flow domain, pay extra attention to the box size. The size of the flow domain box should be large enough that the turbulent wake behind the model as well as the pressure region in front of the model does not reach the boundaries of the box. On the other hand, a large domain will likely increase the simulation expenses. Therefore, use your engineering judgment and/or best practices to size the flow domain.
Running into errors
If the above steps are not followed properly the user can run into errors. The possible reasons for these errors are elaborated here.
Note
If none of the above suggestions solved your problem, then please post the issue on our forum or contact us.