Documentation
Electric transformers are critical to power systems, ensuring efficient voltage regulation and power distribution. Their design and operation must be precise to minimize energy loss, overheating, and performance failures.
Engineers today rely on transformer simulation to analyze, optimize, and validate transformer designs before physical production. Simulation software like SimScale offers advanced 3D modeling tools to solve complex challenges in transformer development. From visualizing electromagnetic fields to analyzing thermal behavior, simulation enables accurate and cost-effective solutions.
This article explores transformer simulation, its importance, and how tools like SimScale improve the design process.
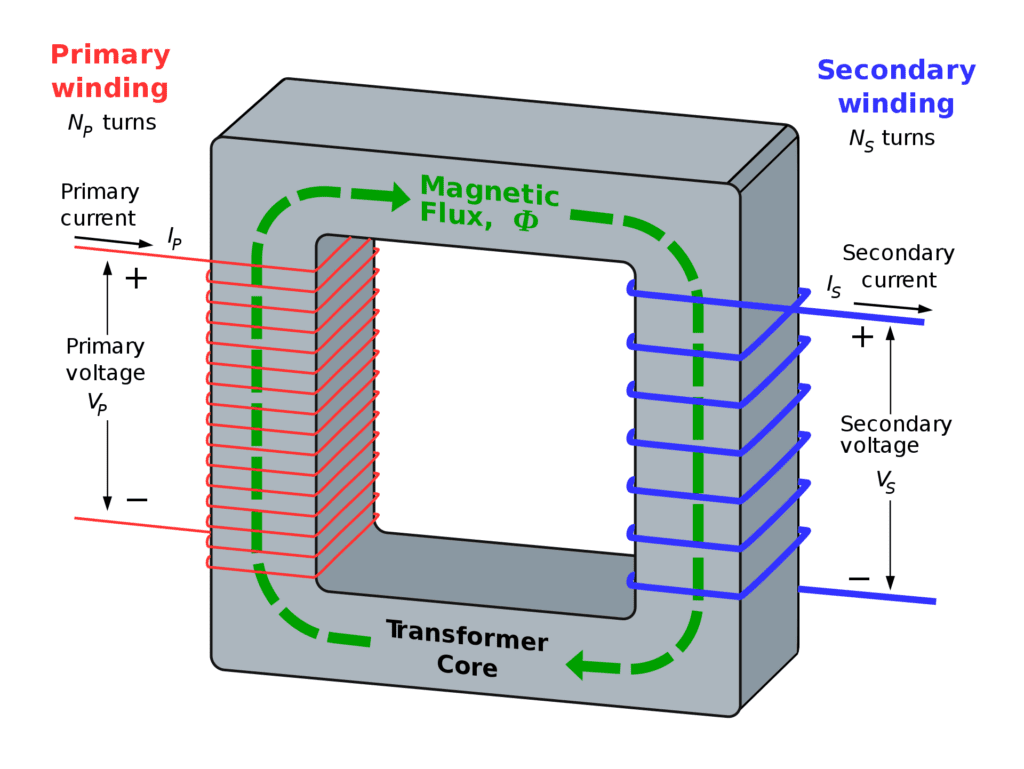
Transformers are devices that transfer electrical energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. Their core components include:
Transformers operate on the principle of mutual induction. When alternating current flows through the primary coil, it generates a magnetic field. This changing field induces a voltage in the secondary coil, transferring power without physical contact.
Their primary function is voltage regulation. Transformers step up the voltage to minimize losses during transmission and step it down for safe distribution to homes, industries, and appliances.
Different transformer types serve specific purposes based on their design and application.
Transformers play a role in renewable energy systems, industrial machinery, data centers, and residential grids. For example, power transformers are critical in wind farms to transmit energy efficiently over long distances.
Designing a transformer involves balancing efficiency, performance, and cost while addressing challenges like energy loss, overheating, and mechanical stress. Traditional physical prototyping can be time-consuming and expensive. Transformer simulation solves these problems by enabling virtual design, analysis, and optimization.
Transformer simulation software provides the tools to identify, analyze, and resolve design challenges efficiently. Benefits include:
By simulating transformers virtually, engineers gain insights into electromagnetic and thermal performance early in the design phase, reducing errors and costly rework.
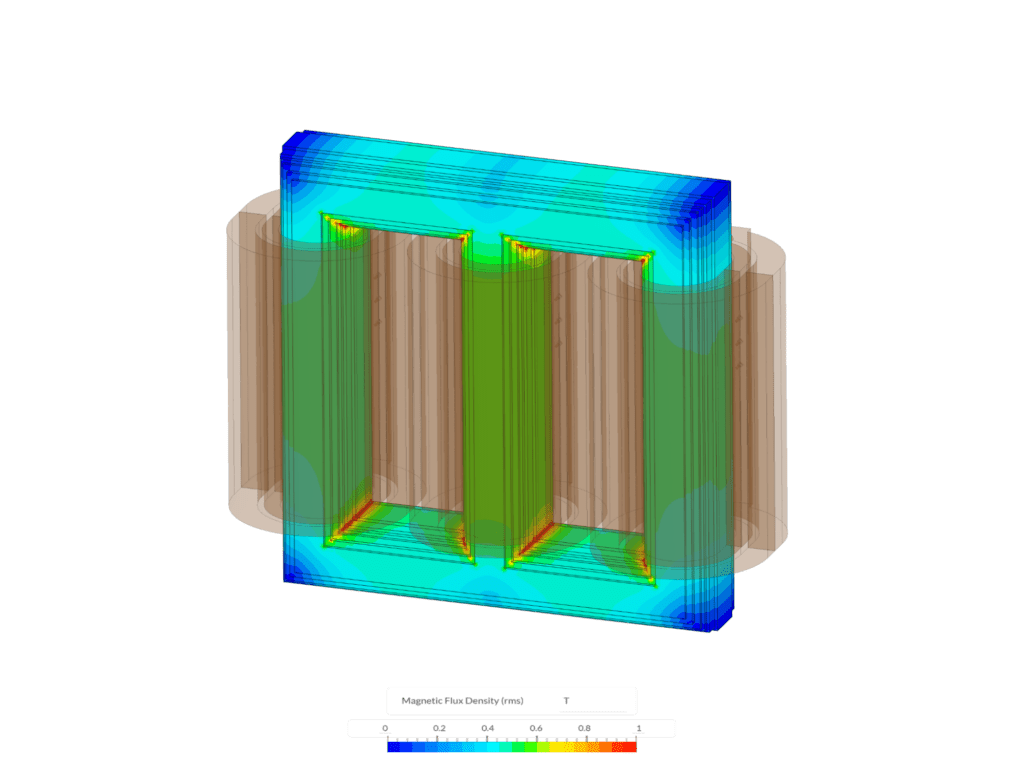
3D simulation tools play a vital role in modern transformer design by providing detailed visualizations and performance analyses. SimScale’s cloud-native platform is one of the most effective tools available for engineers.
3D simulation software allows engineers to model transformers with precision and analyze multi-physics interactions. Simulations can include:
SimScale enables all of this through a cloud-based platform, eliminating the need for specialized hardware. Engineers can test and validate multiple configurations simultaneously, accelerating the design process.
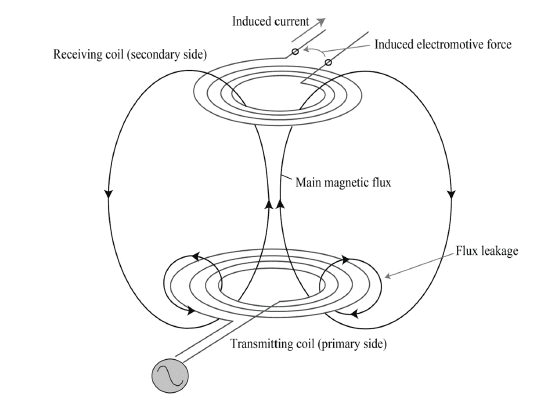
Transformers operate on the principles of electromagnetic induction, a process where changing magnetic fields induce voltage in a conductor. Understanding this principle is essential to optimizing transformer performance.
Faraday’s Law states that a changing magnetic field in a coil induces an electromotive force (EMF) proportional to the rate of change of the magnetic flux. In transformers, alternating current flowing through the primary coil generates a magnetic field that induces voltage in the secondary coil.
The relationship is expressed as:
$$ \text{EMF} = -N \frac{d\Phi}{dt} $$
Where:
This principle underpins the transfer of energy from the primary to the secondary coil. However, the direction of the induced EMF and current is not random. It follows Lenz’s Law, which provides additional insight into energy behavior in transformers.
Lenz’s Law explains the direction of the induced EMF and current in transformers. It states that the induced current will flow in a direction that opposes the change in magnetic flux causing it.
In practical terms, Lenz’s Law ensures energy conservation by creating an opposing force that stabilizes the magnetic field. This opposition regulates how current is transferred between the primary and secondary windings, preventing flux imbalances that could reduce transformer efficiency.
When combined with Faraday’s Law, Lenz’s Law allows engineers to predict and control how transformers respond to alternating currents.
Mutual induction describes how the changing current in the primary coil induces a voltage in the secondary coil. This transfer of energy is the basis of transformer operation.
Simulation tools like SimScale allow engineers to analyze and visualize mutual induction, ensuring accurate voltage regulation and identifying potential inefficiencies.
Electromagnetic field visualization is critical for optimizing core design and reducing losses. SimScale’s transformer simulation capabilities provide detailed insights into:
For example, a simulation can show how altering core material or geometry affects flux density, helping engineers design transformers with maximum efficiency and minimal energy loss.
SimScale stands out as the leading tool for transformer simulation, offering cloud-native capabilities and robust multi-physics analysis. It enables engineers to create accurate virtual models, test different scenarios, and optimize transformer performance without costly prototypes.

SimScale combines advanced capabilities with user-friendly features, making it the preferred choice for transformer simulation. Its cloud-native platform reduces hardware costs and simplifies workflows while delivering precise, actionable results.
In real-world applications, engineers have reported significant time and cost savings by adopting SimScale. Teams can focus on improving transformer performance rather than troubleshooting design issues, resulting in efficient, reliable solutions.
Transformers are not isolated components. They work in conjunction with generators, motors, and power grids to ensure seamless power generation, transmission, and distribution. Simulation plays a key role in optimizing transformers within these interconnected systems.
Transformers are integral to systems involving generators and motors.
For instance, engineers designing transformers for electric motor systems can use SimScale to evaluate electromagnetic behavior, ensuring motors receive consistent power with minimal losses.
Modern power grids rely on smart transformers to handle fluctuating energy demands and renewable energy integration. Simulation allows engineers to:
SimScale enables engineers to simulate real-world grid scenarios, helping them design transformers that maintain efficiency even under fluctuating loads and changing power demands.
Designing reliable, efficient transformers requires precision and deep insights into electromagnetic, thermal, and structural behaviors. Physical testing alone cannot meet modern engineering demands for speed and cost-efficiency.
Transformer simulation software like SimScale empowers engineers to visualize, analyze, and optimize designs before physical prototypes are built. SimScale’s cloud-native platform eliminates the need for specialized hardware, reduces costs, and accelerates development cycles.
Key benefits include:
Transformers are essential to modern electrical systems, from renewable energy grids to industrial applications. Optimizing their performance requires the right tools.
Start using SimScale today to simulate, improve, and validate your transformer designs with precision.
Last updated: November 10th, 2025
We appreciate and value your feedback.
What's Next
What is Electromagnetic Induction?Sign up for SimScale
and start simulating now