Documentation
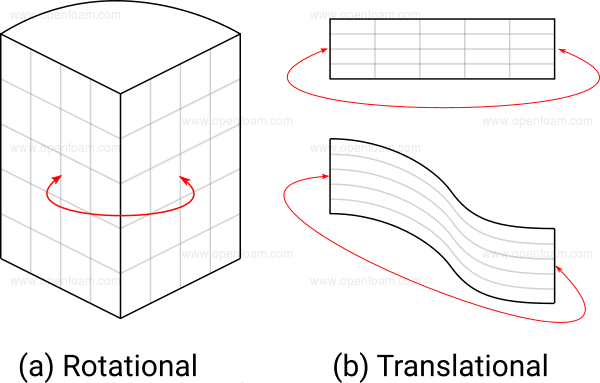
The Periodic or cyclic boundary condition (BC), is used in computational fluid dynamics simulations. It defines a cyclic/repeating situation of the flow across the boundary surface. For this condition, it is mandatory to select two boundary faces that will be treated as if they are physically connected. The flow exiting/entering from one face then enters/exits the other face.
Generally, this boundary condition is used to approximate infinitely long domains into smaller ones.
Symmetry Boundary Condition
Please note that Periodic boundary condition is different from the Symmetry boundary condition for computational fluid dynamics and also the Symmetry plane boundary condition for finite element analysis. You can read more about them here.
The settings panel for the Periodic boundary condition is as follows:
Besides the assignment of the faces no other numerical input is required from the user.
Key points to remember before applying the periodic boundary condition:
Speaking math, the flux across the two faces is same in magnitude with opposite signs.
Such a mesh can be ensured in SimScale currently using the standard mesher. To know more about the standard meshing algorithm click here.
Some common examples where the periodic condition can be used are heat exchangers and on pipes.
Note
SimScale supports only the translational periodic boundaries. This means turbines or fans cannot be used with this boundary condition.
Last updated: August 24th, 2022
We appreciate and value your feedback.
Sign up for SimScale
and start simulating now