Error
The machine ran out of memory. Please choose a larger machine by increasing the number of computing cores or reduce the fineness of your mesh.
What Happened?
This error occurs when the machine selected for your simulation runs out of memory. This means that the machine selected was too small for the simulation to be able to run until it is finished.
What Could Be the Possible Reason?
The machine can run out of memory because of several reasons, as stated below:
- The size of the flow domain: The flow domain is too large for the machine to run a simulation, therefore the simulation requires a larger machine.
- Element size: The element size is too small which produces a large mesh size.
- The selected number of cores: The number of cores you selected for the simulation run is too small.
- Radiation: The analysis type includes radiation, and the number of faces in the CAD model is too high.
What Can I Do Now?
You can solve the problem in several ways, as stated below:
Best Practices
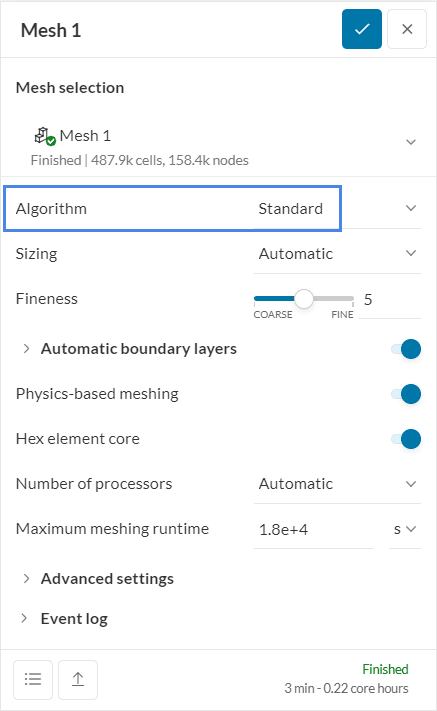
Use the Standard Mesher
The standard mesher for CFD simulations is an automatic meshing algorithm that produces a three-dimensional unstructured mesh, consisting of tetrahedral and hexahedral elements.
You can do this by going to the Mesh and changing the Algorithm to Standard. This will change the meshing algorithm to SimScale’s standard meshing algorithm which takes into account the geometric properties of the model.
Important Information
- For mesh related solutions, the mesh needs to be regenerated and a new simulation needs to be run. Note that the coarser the mesh, the faster it is to generate.
- After the number of cores has been increased, a new simulation run will need to be created to implement the change to the number of assigned cores.
Enlarge the Size of Elements
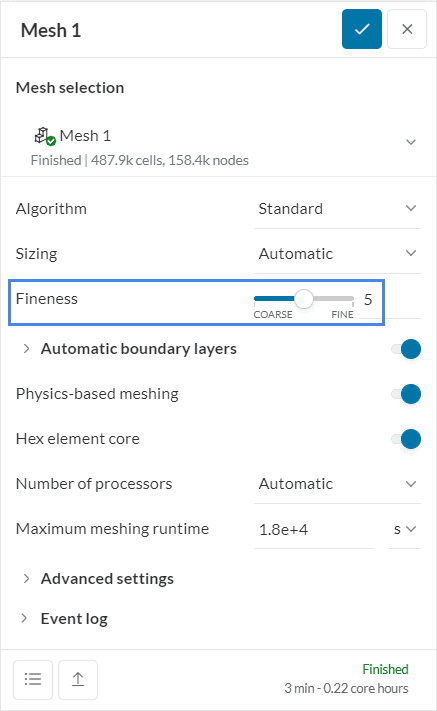
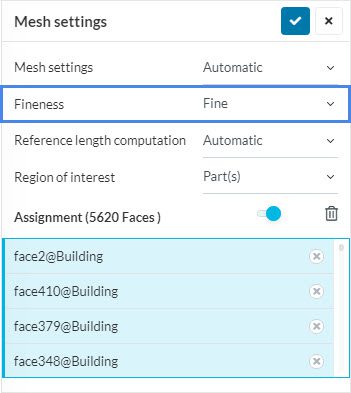
The larger the size of the elements, the lower the number of elements required, thus less memory is required. You can do this by decreasing the fineness level of the mesh. It is better to decrease the mesh by one level to find the balance between good mesh and memory usage.
This can be done by going to the Mesh and decreasing the Fineness level. The fineness level will be increased according to the features of the geometry. It is important to remember that decreasing the fineness level will make the mesh generation faster.
Reduce Radiation Resolution
When radiation is involved in the simulation setup lowering the radiation resolution to a coarser level can be effective in freeing the machine memory.
Increase the Number of Cores
A larger number of cores will increase the memory available for the simulation, as it increases the capacity of the machine to run the computation. Currently, SimScale supports machines with a capacity of up to 192 cores.
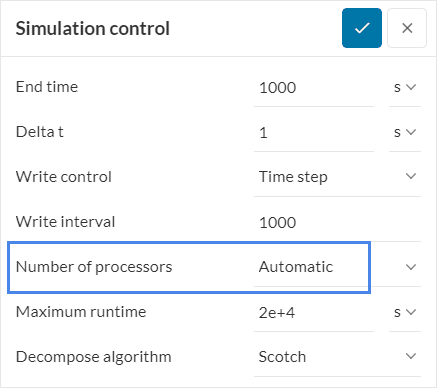
You can do this by going to Simulation control and changing the number in the Number of processors.
Clean the CAD Model
The analysis type, which includes radiation, requires higher memory. The memory requirement for the radiation calculations increases with respect to the number of fluid faces in the CAD model. You can consider simplifying the CAD model by reducing the number of faces, such as small faces on the fluid region.
PWC and LBM Simulations
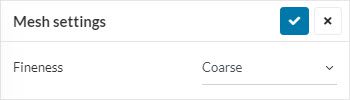
For an LBM or PWC simulation, if the user encounters this error, the solution is to reduce the Fineness of the mesh and this can be done in the Mesh settings of the simulation.
Structural Simulations
Decrease the Number of Parallel Processes
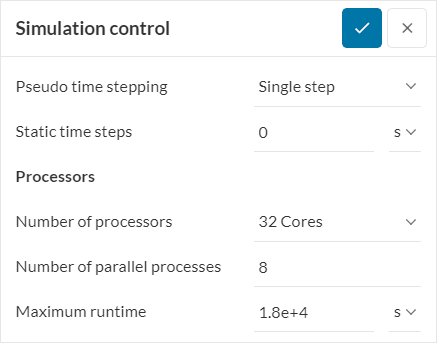
For the structural solvers, in addition to the above actions on the mesh and model details, the memory error can be solved by decreasing the number of parallel processes. This can be done in the Processors section of the Simulation Control panel:
The rationale behind this action consists in that for a given machine size, defined by the Number of processors, the total memory is shared by the Number of parallel processes. If the amount of memory for one of the processes is not enough to complete the computation, its memory share can be increased, by decreasing the Number of parallel processes.
Optimize the Contacts
A common culprit of high memory consumption is contact relations. If the model has a high number of nodes assigned to contacts, such as bonded, sliding, or cyclic symmetry, the model size grows considerably, elevating the memory consumption.
An optimization can be achieved if you identify parts that are connected by bonded contacts and are made of the same material. These parts can be fused together in CAD mode, getting rid of the bonded contact and the related memory consumption.
Important Information
If none of the above suggestions solved your problem, then please post the issue on our forum or contact us.