A heat sink is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device to a fluid medium, where it is then dissipated away from the device. Through this process, the heat sinks play a crucial role in the temperature regulation of the device, preventing overheating. Heat sinks are commonly used in electronics, where cooling and temperature regulation is a crucial factor to ensure the effectiveness of the product.
The Raspberry Pi is a series of small single-board computers developed in the United Kingdom by the Raspberry Pi Foundation to promote the teaching of basic computer science in schools and in developing countries. [1]
As with all electronics, a Raspberry Pi designer needs to ensure that the product receives adequate cooling. This is where a heat sink is integrated.
SimScale allows heat sink designers to test different designs in parallel, 100% in the browser, giving flexibility, collaboration options and access to high computing power— up to 32 cores—from a normal PC or laptop. This allows designers to make optimization decisions based on the simulations’ results and deliver the best possible design. We have dedicated one page to all advantages of online simulation software.
Raspberry Pi Heatsink Thermal Analysis of a Raspberry Pi Heat Sink
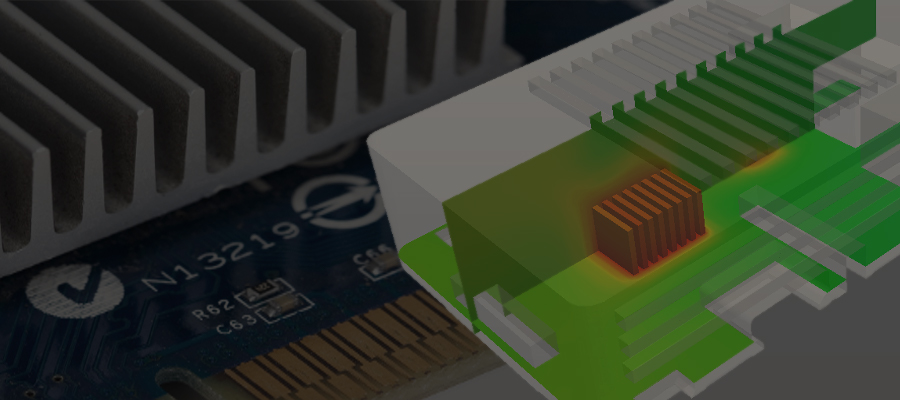
This conjugate heat transfer analysis was performed on a Raspberry Pi enclosure by having a processor with a mounted heat sink over it. The focus of this simulation is to study the cooling performance to determine if it meets the cooling requirement of the Raspberry Pi.
In terms of results, this study clearly shows that the cooling is still quite effective under passive environmental conditions with the use of the designated heat sink.
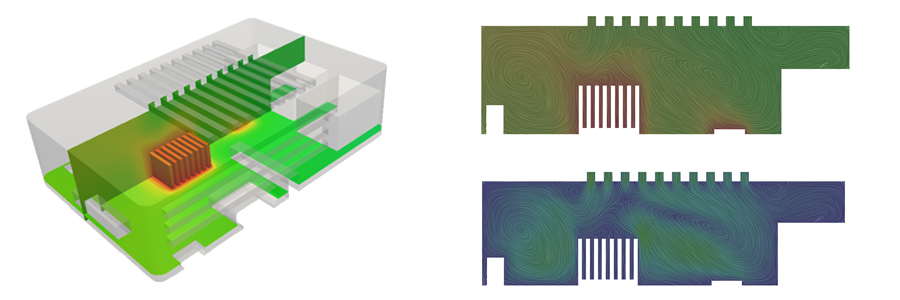
The contours below show the temperature on a 3D model cutout (left), the temperature on a 2D slice (top right) and the velocity distribution plot (bottom right).
To learn more about cooling and temperature regulation, visit our dedicated heat sink page or read this case study. Also, we invite you to give simulation a try with our free community account.
This free infographic illustrates how engineers can develop the best cooling strategy using thermal simulation. Download it for free.
References
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Raspberry_Pi