“Manufacturers must embrace continuous adaptation or risk falling behind.”
That’s a strong sentiment to start an article with. And, really, just a fancy way of saying “adapt or die”.
But is it true?
The industrial manufacturing sector is evolving rapidly. Companies are contending with a wave of disruption;
- The race to decarbonize
- Relentless digital transformation
- Fierce global competition
These challenges are fundamentally reshaping how businesses design, build, and maintain products.
Traditional engineering approaches are often no longer sufficient. Organizations must adopt digital-first tools and strategies to drive agility, efficiency, and innovation. Simulation, especially when integrated early in the design process, is emerging as a cornerstone of this transformation.
Industrial Manufacturing Trends: Macro Trends Shaping the Industry
The industrial machinery landscape is being redefined by a series of converging macro forces. There’s a large range of manufacturing industry trends shaping the sector;
- Environmental regulations
- Digital disruption
- Rise of artificial intelligence
- Electrification of equipment
- Emerging technologies (including smart factories and advanced automation)
Labor shortages, global supply chain disruptions, and workforce concerns are additional significant macro forces impacting the industry and influencing strategic decisions.
Company reports provide valuable insights into these macro trends, offering authoritative data on corporate strategies, investments, and sustainability initiatives.
These trends are placing new demands, and opening up new opportunities, for manufacturers.
Below, we break down the seven most transformative forces currently shaping the industry. Understanding and acting on these trends is key to remaining competitive in an increasingly complex and volatile global environment.
1. Digitalization & Industry 4.0
The fourth industrial revolution is here – and manufacturers are rapidly adopting digital tools to modernize operations and gain a competitive edge!
At the core of this transformation is the integration of cyber-physical systems, digital twins, and IoT sensors. These enable real-time data collection, predictive maintenance, and optimization across production lines. Yet, integrating new technologies with legacy systems presents challenges, highlighting the need for infrastructure upgrades.
Simulation plays a vital role by offering a virtual testbed to model, evaluate, and refine systems before implementation. For example, engineers can explore hundreds of design variations in a single afternoon—an efficiency that used to take weeks with physical prototypes.
2. Sustainability & Regulatory Compliance
Sustainability is no longer a corporate side project; it’s a front-and-center driver of design and engineering decisions. New ESG mandates are forcing companies to evaluate their energy use, emissions output, and materials sourcing at every step of the product lifecycle. Many manufacturers are now adopting circular economy principles to reduce waste, conserve resources, and promote eco-friendly production methods.
Lifecycle Assessments (LCA) are increasingly mandatory for product approvals in Europe and North America. By modeling these assessments digitally through simulation, companies can understand the environmental impact of a product before it’s built.
In addition to monitoring energy use and emissions, companies are increasingly turning to renewable energy sources such as solar and wind to achieve sustainability goals, reduce emissions, and support environmentally friendly production practices.
Beyond compliance, sustainability is also a competitive differentiator. Customers are demanding greener machinery, and investors are rewarding firms that show measurable ESG progress. Simulation allows manufacturers to optimize for sustainability – minimizing energy consumption, maximizing reuse, and streamlining thermal and fluid efficiencies.

3. Electrification and Energy Transition
The industrial push toward electrification is reaching a tipping point. Governments around the world are subsidizing the transition away from fossil fuels, and industrial OEMs are responding with urgency. Electric motors are replacing combustion engines, and hydrogen combustion systems are being piloted across sectors like heavy machinery and chemical processing.
But the move isn’t as simple as swapping engines. Engineers must address a new generation of design challenges: how to manage battery heat, balance energy loads, and ensure durability under new mechanical stresses. Simulation accelerates this learning curve by giving teams the ability to evaluate component behavior under various load conditions and extreme environments – long before field testing.
One growing trend is the integration of thermal and structural simulations to evaluate how electrified components behave under real-world operating pressures, such as rapid load cycling or ambient temperature variation.
4. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Product Development
Artificial intelligence is shifting from a buzzword to a mission-critical capability. Predictive analytics are already helping engineers detect anomalies and preempt failure modes, while machine learning is being used to continuously optimize designs based on past performance data. AI is also increasingly used to enhance the production process by detecting anomalies in real time and optimizing maintenance and safety procedures.
Generative design, a form of AI that explores all possible permutations of a solution, is also gaining traction. Combined with simulation, this creates a feedback loop where AI proposes options, simulation tests them, and the best ideas are automatically refined and selected.
AI-assisted simulation is especially valuable in high-variability product environments, like HVAC systems or turbomachinery, where the number of possible configurations is vast and traditional methods fall short.
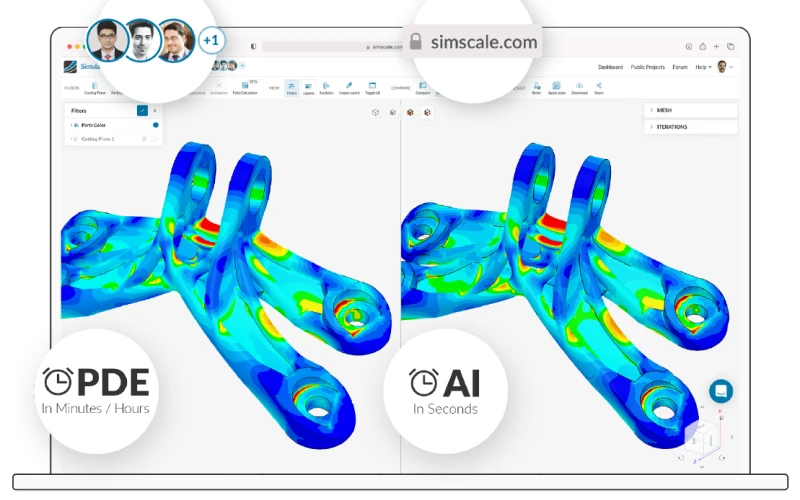
5. Market Dynamics and Global Competition
The global landscape for industrial manufacturers is more complex and cutthroat than ever. Shorter project timelines, rising material costs, and demands for customization are all compounding pressure on engineering teams.
Customers expect tailored solutions, yet still want fast turnarounds and competitive pricing!
Simulation allows companies to meet these demands by reducing cycle times and increasing iteration velocity. In this environment, speed is not just a competitive advantage – it’s a requirement for survival.

6. Global Supply Chains: Resilience and Transformation
The manufacturing industry is undergoing a profound transformation as global supply chains face unprecedented challenges and opportunities. Recent supply chain disruptions, most notably those triggered by the COVID-19 pandemic, have exposed vulnerabilities in traditional supply chain management strategies. As a result, manufacturing companies are reimagining their approach to ensure greater supply chain resilience and adaptability.
To address these challenges, leaders in the manufacturing sector are turning to advanced technologies. These tools enable real-time monitoring and predictive analytics, allowing companies to anticipate disruptions and optimize production processes.
Another key trend is the reevaluation of global supply chains, with many manufacturing organizations diversifying their supplier base and exploring nearshoring options. By reducing reliance on single-source suppliers and bringing production closer to end markets, companies can better manage risks and respond more quickly to market shifts.
Digital transformation is at the heart of this evolution. Investments in smart supply chain management systems empower manufacturers to make data-driven decisions, streamline logistics, and enhance supply chain resilience. As the manufacturing industry continues to adapt, those who embrace these innovations will be best positioned to thrive in a dynamic global environment.
7. Additive Manufacturing: Redefining Production Paradigms
Additive manufacturing is fundamentally reshaping the manufacturing industry by challenging and redefining traditional production paradigms. This innovative technology enables manufacturers to create highly complex products with remarkable efficiency, significantly reducing material waste and streamlining production processes.
As the industry evolves, additive manufacturing is also influencing workforce development. Efficient workforce training programs are being designed to upskill employees in the use of advanced manufacturing equipment, while augmented reality tools are being integrated to support hands-on learning and boost human capabilities on the factory floor.
Looking ahead, additive manufacturing is set to play a pivotal role in the future of industrial manufacturing. By enabling manufacturers to optimize production processes, reduce costs, and deliver tailored solutions, 3D printing is helping companies maintain a competitive edge in an increasingly complex market landscape.
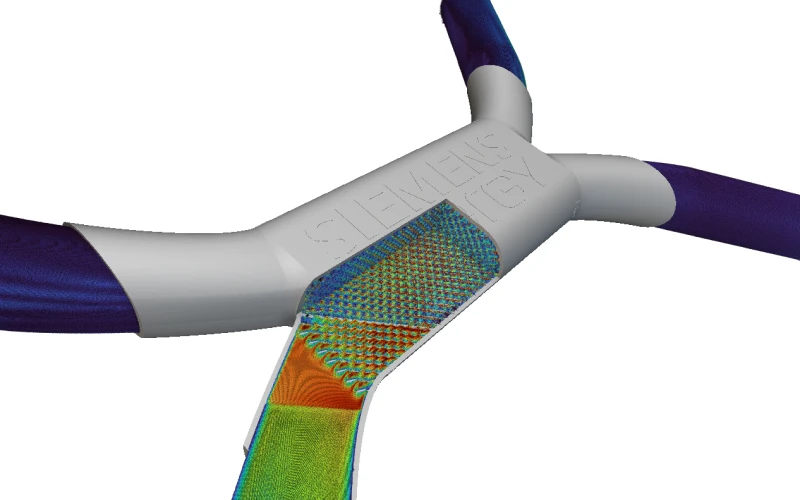
Siemens Energy used SimScale to rapidly iterate it’s 3D printed heat exchanged design for heat transfer efficiency and pressure drop optimization.
Simulation as a Strategic Response to Industry Challenges
Simulation has rapidly evolved from a niche engineering function to a core driver of industrial competitiveness. It enables teams to virtually prototype, test, and optimize systems in a fraction of the time, and at a fraction of the cost, compared to traditional physical methods.
Companies that integrate simulation early in the design process are seeing transformative results, from shorter development cycles to lower energy consumption and fewer field failures. But its applications don’t stop at product design. Simulation is increasingly being used throughout the lifecycle—from maintenance strategy to operational troubleshooting.
Early-Stage Simulation for Competitive Advantage
By incorporating simulation from the concept phase, manufacturers can detect design flaws, explore performance limits, and validate ideas long before production.
Bühler Group used cloud-native simulation to test 60 design variants in just two weeks—cutting lead times and boosting collaboration across five international engineering teams.
Hazleton Pumps reported a 99% reduction in development time, and savings of $40,000 per pump, by optimizing structural components before any prototypes were built.
These are not edge cases—they represent a broader shift in how modern manufacturers are approaching engineering.
Cloud-Native Design & Simulation Platforms
The shift to cloud-native platforms is removing historical barriers to simulation. Engineers no longer need access to costly high-performance computing infrastructure or specialized software environments. Platforms like onshape and SimScale allow design and simulation to happen directly in the browser with enterprise-grade accuracy.
Key benefits include:
- Global collaboration: Teams in different regions can share and iterate on models in real time
- Scalability: Run multiple simulations simultaneously to explore more design options
- Integration: Seamlessly connect with popular CAD tools and PLM systems
This shift is democratizing access to simulation and expanding its use across disciplines.
Simulation Beyond Design: Operations & Maintenance
Perhaps the most exciting frontier is the extension of simulation into operational decision-making. Companies are using simulation to diagnose real-time plant issues, fine-tune performance, and even develop predictive maintenance strategies.
- Methanex used simulation to redesign a leak containment system in under a day—avoiding a $3.5M outage.
- Nalco Water achieved a 70% reduction in unplanned downtime at a paper mill by simulating and optimizing a faulty nozzle.
Simulation in these contexts isn’t just about design—it’s about keeping revenue-generating systems online and operating efficiently.
“We use simulation not just for design, but for real-time operational fixes.”
Industry-Specific Trends and Applications
Simulation delivers value across nearly every segment of industrial machinery. Technology investments in simulation and digital tools are enabling sector-specific innovation and efficiency, helping companies stay competitive. From pumps and fans to compressors and valves, virtual testing and verification are allowing engineers to solve sector-specific problems quickly and effectively.
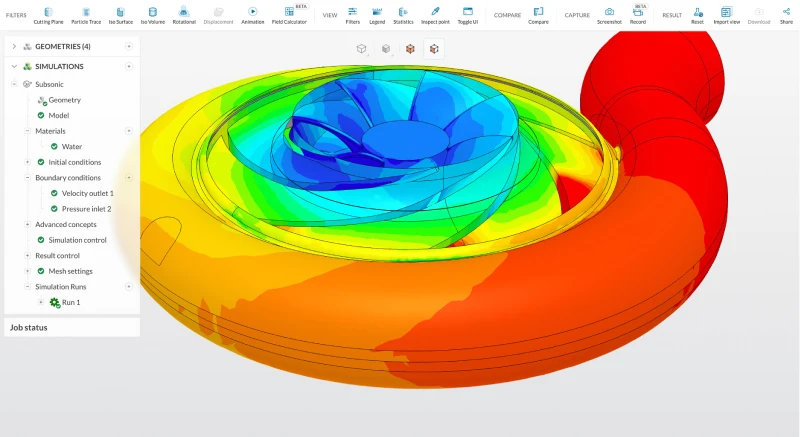
Turbomachinery and Fluid Systems
Pumps, compressors, and turbines are at the heart of many industrial systems, and notoriously sensitive to flow conditions. With tools like SimScale, engineers can run high-fidelity simulations in hours rather than days to:
- Generate pump and fan curves
- Analyze cavitation and efficiency
- Predict structural wear due to flow dynamics
These insights lead to more reliable equipment, lower energy consumption, and extended lifespan.
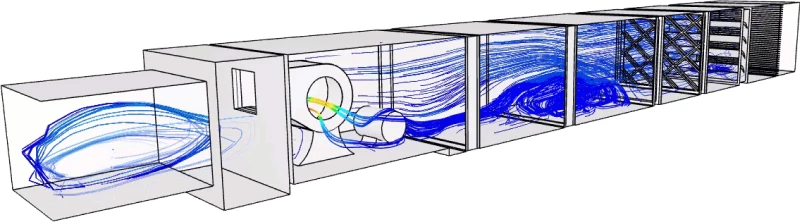
HVAC Innovation and Compliance
HVAC engineers must balance performance, efficiency, and compliance with increasingly strict energy and indoor air quality standards.
Fusion Modulair used cloud simulation to evaluate an entire building’s airflow dynamics, completing 22,000+ core hours of analysis in just three weeks. This enabled them to:
- Ensure compliance with ASHRAE and LEED
- Optimize comfort and energy use
- Reduce post-installation rework
Valve, Flow Control, and Process Optimization
In flow control systems, even small inefficiencies can lead to large losses. Simulation allows engineers to:
- Optimize valve shapes and materials
- Analyze pressure drops and flow rates
- Test electromagnetic actuation mechanisms
This results in faster delivery of custom valves, reduced failure rates, and more accurate control systems.
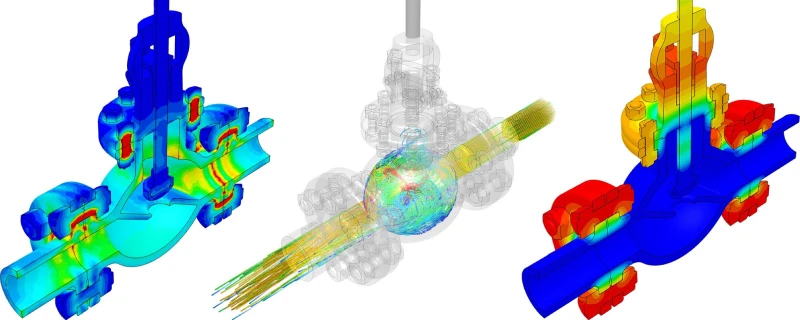
Renewable Energy and Sustainable Design
Simulation is also accelerating the development of next-gen renewable technologies.
- Cryo Pur cut simulation time from 26 hours to 1 using parallel cloud computing, enabling faster iteration on cryogenic systems
- Energyminer used multiphase simulations to optimize flow and power output in micro-hydro systems—reducing physical prototyping needs and time to market
These gains are helping smaller innovators compete with industry giants.
Future Outlook: Building Resilience Through Innovation
As manufacturers prepare for the future, resilience and adaptability will define success. The companies best positioned to thrive will be those who build simulation into their DNA across product development, operations, and strategic planning.
“Simulation is no longer a niche tool—it’s the backbone of industrial innovation.”
Looking ahead, expect to see even deeper integration of AI, digital twins, and real-time performance monitoring. Simulation will play a critical role not just in creating the next generation of equipment, but in ensuring it operates efficiently, sustainably, and safely throughout its lifecycle.
Conclusion
To lead in 2025 and beyond, manufacturers must:
- Embrace early-stage simulation
- Invest in cloud-native platforms
- Align innovation with sustainability and compliance
Simulation empowers teams to innovate faster, cut costs, and reduce risk—all while delivering products that meet the highest standards of performance and sustainability.
The leaders of tomorrow are simulating today.
📢 Ready to modernize your workflows? Explore simulation with SimScale now.