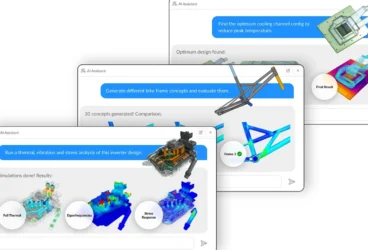
Artificial intelligence dominates the conversation in nearly every industry, and engineering is no exception. The promise is immense: accelerated innovation, hyper-efficient workflows, and the ability to solve previously intractable problems.
AI in engineering is only just starting to break out into the mainstream. We recently surveyed 300 engineering leaders and we found that only 7% had mature AI programs in place, with 42% actively working on pilots, but over half having still not yet started anything serious.
But while we saw widespread acknowledgement that AI in engineering has huge potential, only 3% of companies adopting it are already reaping the significant rewards that are possible.
Put simply, there is a huge opportunity for engineering organizations to build a competitive advantage by adopting this technology in the right way.
This article cuts through the noise to showcase seven ways that we see AI delivering value to our customers. These are not futuristic concepts; they are tangible solutions that directly address the most time-consuming, error-prone, and knowledge-intensive aspects of engineering.
Simulation Democratization: AI for Every Engineer
Traditionally, physics simulation has been a specialized field, confined to a few experts with access to expensive software and hardware that’s complicated to learn and use. This creates a dual bottleneck: projects stall waiting for expert review, and deep engineering knowledge is difficult to scale across the team.
The AI Solution: The goal of simulation democratization is to put these powerful tools safely into the hands of every engineer. Cloud-native platforms already provide much easier browser-based access, but the real key is Agentic AI acting as a force multiplier for expertise. It captures the proven methods of senior engineers and embeds them into reusable templates and guided workflows. This gives every engineer an AI-powered co-pilot that walks them through complex processes step-by-step, interacting using natural language. Opening up access to simulation in this way ensures consistency and reduces errors, while scaling knowledge across the entire organization.
RFQ and RFP Automation: Winning More Bids
Responding to a Request for Quote (RFQ) or Request for Proposal (RFP) is a high-pressure, make-or-break moment. Engineering teams must quickly assess feasibility, optimize designs, and produce reliable cost estimates under tight deadlines. This often leads to rushed proposals, reduced win rates, and shrinking profit margins.
The AI Solution: AI-driven automation transforms the RFQ process. An Agentic AI can read an RFQ, instantly generate relevant design concepts, and automatically validate them using physics simulation. This allows teams to explore multiple options, identify cost and feasibility risks early, and package proposal-ready reports in hours instead of days.
Accelerating R&D and Product Innovation
Traditional R&D is slow, expensive, and risky. Heavy reliance on costly physical prototyping and limited resources means teams can only explore a handful of design options, leaving breakthrough ideas undiscovered and inflating budgets.
The AI Solution: AI-enhanced simulation tackles R&D challenges on two fronts: cost and speed. It enables virtual prototyping, where thousands of digital experiments replace physical models to cut material waste and lab expenses. Simultaneously, it powers massive design space exploration, where generative workflows create and test thousands of concepts in parallel. This combined approach allows teams to compress development timelines from months to days while making smarter, more cost-effective design choices.
Agentic Workflow Automation: Connecting the Dots
Engineering processes often involve a maze of manual handoffs between different tools and teams for tasks like geometry prep, simulation, and reporting. Each step introduces potential delays and human error, wasting valuable engineering time that could be spent on innovation.
The AI Solution: Agentic workflow automation uses AI to connect these disparate steps into a single, seamless process. AI agents can coordinate everything from CAD input and multi-physics analysis to optimization and reporting, all without manual intervention. By integrating with existing tools like CAD and PLM systems, these automated workflows plug directly into established engineering processes. Check out our recent webinar: The Rise of AI Agents in Engineering – What Can We Expect?.
Real-Time Digital Twins: Bringing Designs to Life
Digital twins are powerful, but traditional versions are difficult to implement, often requiring heavy modeling effort and costly, manual data integration. As a result, the insights they provide often lag behind reality.
The AI Solution: AI is making real-time digital twins a practical reality. The key is using lightweight Physics AI surrogates – AI models trained on high-fidelity simulation data that can run in real-time. By connecting these surrogates to live sensor data from products in the field, engineers can get instant predictive insights into performance, spot potential failures before they happen, and feed real-world data back into the R&D process.
AI in engineering is here – it just needs to get from the lab into the loop
The engineering industry’s gap between AI ambition and execution is a clear signal that a focused approach is needed. The path to closing this gap is not about “doing AI” in the abstract, but about deploying it with purpose. It’s likely that your organization is already pursuing initiatives like those explored in this blog, AI simply redefines what is possible to achieve with them:
| Use Case | Why? | AI-Powered Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Simulation Democratization | Simulation is a bottleneck, limited to a few experts. Knowledge is siloed and difficult to transfer. | Every engineer can access simulation, guided by a GenAI “co-pilot” that captures expert methods for safe, consistent use. |
| 2. RFQ/RFP Automation | Manual, rushed proposals based on limited design exploration, leading to lower win rates and margins. | AI agents can automatically generate and validate multiple design concepts, producing data-rich proposals in hours. |
| 3. Accelerating R&D and Innovation | R&D is slow and expensive, relying on physical prototypes and limiting design exploration. | AI enables massive virtual testing, cutting costs and compressing development cycles from months to days. |
| 4. Agentic Workflow Automation | Disconnected, manual processes with handoffs between different software tools, causing delays and errors. | AI automates the entire end-to-end workflow, crossing different platforms from CAD to simulation to reporting, without manual intervention. |
| 5. Real-Time Digital Twins | Digital twins are slow, expensive to build, and struggle to keep up with real-world conditions. | Lightweight, AI-powered “surrogate” models connect to live sensor data for real-time predictive insights. |
The use cases for AI in engineering detailed in this blog—from further democratizing simulation to automating commercial responses—are tangible, real-world applications that directly solve the most significant productivity bottlenecks in the modern engineering simulation process. They are the practical bridge that connects the ambition for AI to its successful execution.
For engineering leaders, the call to action is to shift from tactical experimentation to strategic transformation. This means investing in the open, cloud-native platforms capable of supporting this new generation of embedded, agentic, and collaborative AI. The ultimate goal is not to replace the invaluable expertise of engineers, but to fundamentally enhance it. By creating “machine-in-the-loop” workflows, we can supercharge their creativity, multiply their impact, and free them to focus on what they do best: solving the world’s most complex challenges and engineering the irreplaceable.
Ready to see how AI can transform your engineering workflows?
Get in touch with one of our specialists to learn how you can start applying these use cases today.