For today’s engineering leaders, the operating environment has become a crucible of competing pressures – pun fully intended!
The market demands unprecedented speed, pushing for shorter design cycles and faster time-to-market. Simultaneously, products are becoming exponentially more complex, integrating sophisticated electronics, software, and new materials.
The need to optimize product performance is more critical than ever to meet these increasing demands.
Add to this the intense pressure to drive down costs all while meeting stringent sustainability and regulatory targets that have become a prerequisite for market access.
This is the engineer’s dilemma: a delicate, high-stakes balancing act between speed, cost, and sustainability.
Traditional, sequential engineering workflows and legacy software tools, which have served the industry for decades, are proving insufficient to navigate this new reality.
The strategic response cannot be another incremental tool; it must be a systemic shift toward a more integrated, intelligent, and data-centric ecosystem.
The engineering design process itself is being transformed, as AI-driven design integrates with ideation, creation, validation, and manufacturing to deliver innovative solutions more efficiently.
This is where Artificial Intelligence (AI) transitions from a futuristic buzzword to a present-day strategic imperative. By embedding AI into the core of the design process, organizations can move beyond making difficult trade-offs and begin to achieve multiple objectives at once, creating a powerful and sustainable competitive advantage.
The Modern AI Toolkit: From Augmenting Insight to Generating Innovation
To deploy AI effectively, it’s crucial to understand its distinct capabilities.
For engineering leaders, the AI toolkit can be broadly divided into two primary functions:
- Predictive AI, which uses data -often analyzed by machine learning algorithms—to forecast future outcomes, and
- Generative AI, which acts as a creative partner to autonomously generate novel design solutions, guided by specific design requirements to ensure fit, form, and function.
Predictive AI: From Reactive Fixes to Proactive Strategy
Predictive AI is about moving your organization from a reactive to a proactive posture. Its core function is to analyze vast datasets, including historical data, to predict outcomes faster than traditional methods, enabling proactive problem-solving and risk mitigation. By leveraging historical data, predictive AI systems train and validate predictive models that can forecast equipment failures and optimize operations. In the industrial sector, this has several high-impact applications, most notably in predictive maintenance. By analyzing real-time data from equipment, AI can anticipate component failures before they occur, minimizing costly unplanned downtime.
The business impact is not theoretical; it’s measured in millions of dollars saved.
Predictive AI enables project managers to make more informed decisions by providing accurate forecasts and actionable insights.
Operational Continuity at Methanex: When faced with a potentially high-risk leak in one of its methanol production plants, the company’s reliability engineering team and project managers used cloud-native simulation to analyze the fluid dynamics and validate a new containment component. They designed, simulated, and verified a solution within a single business day, preventing a forced outage of the unit and saving an estimated $3.5 million in production losses.
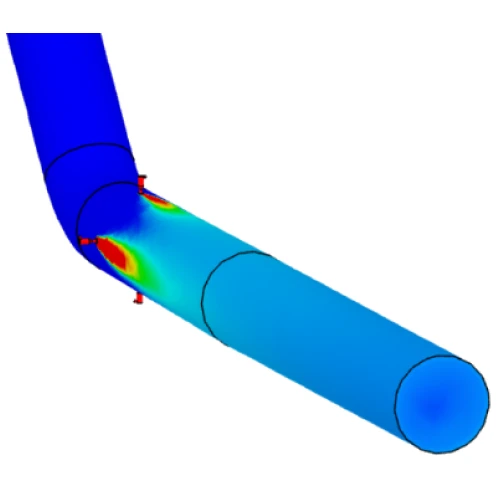
Downtime Reduction at Nalco Water: In another high-stakes scenario, Nalco Water used CFD simulation to urgently diagnose and fix a faulty water nozzle that was causing significant downtime at a large paper mill. By optimizing the nozzle design, the company achieved a 70% reduction in unplanned downtime, translating to an annual saving of $10 million for their client.
We have been using SimScale for FEA, CFD, and thermal analysis of our methanol production plants and components. We had a potentially high-risk situation with a leak in one of our plants and were able to use SimScale to turn around a verified solution within one business day. Without SimScale, we would have had to force an outage of the unit, costing time and significant production losses.
— Reliability Engineer at Methanex
Generative AI Models: Your Partner in Design Exploration
While predictive AI uses past and present engineering data to predict future outcomes, generative AI is a revolutionary force that changes how that future is created. It represents a paradigm shift in the way engineers interact with software and the capabilities of the workflows they make use of.
Powered by deep generative models, Engineering AI enables engineers and designers to define engineering design problems using higher level descriptions and have the AI autonomously explore the entire design space to generate a range of optimized designs.
Natural Language: A Force for Democratization
Using Gen AI powered agents to communicate with engineering software lessens the learning curve for new users of a software tool, allowing them to communicate intent and the engineering parameters and constraints, letting an agentic AI do the rest.
Guiding the Application of Company Best Practices
Gen AI can address the challenge of maintaining simulation quality across distributed teams. It acts as a digital mentor that reinforces company best practices and prevents common errors during workflows. By learning from successes and mistakes, the AI drives continuous improvement and consolidates organizational expertise for users of all experience levels.
Collaborating With Other Agents
The potential of Generative AI is greatest when agents collaborate with each other. We recently demonstrated a proof-of-concept where specialized agents from SimScale and Generative Engineering worked together to autonomously explore and iterate on designs. This form of digital teamwork will transform tool interoperability, leading to seamless, agent-powered engineering workflows in the near future.
Automating RFQ Responses
A key future application for this technology is automating RFQ (Request for Quotation) responses. Engineering agents will be able to automatically interpret customer requirements, run simulations, and validate a design proposal against performance criteria. This offers significant value to organizations handling high volumes of RFQs by reducing manual work, accelerating response times, and freeing engineers for more creative tasks.
Accelerating design exploration and generation
With predictive AI delivering near-instantaneous design evaluation, and agentic AI massively accelerating and automating workflows, we start to see a transformation of New Product Development (NPD) programs:
- Define the Problem: The engineer inputs the high-level parameters and constraints. This includes performance requirements (e.g., load conditions, stiffness), material options, cost targets, cost goals, and, crucially, the available manufacturing methods (e.g., 5-axis CNC machining, casting, additive manufacturing).
- Generate Solutions: The AI algorithm then explores all possible permutations, using existing designs and previous designs as foundational input data for generative models. It generates hundreds or even thousands of novel design options that satisfy all the defined constraints. The resulting geometries are often “organic” or “skeletal,” mimicking nature’s efficiency by placing material only where it is structurally necessary. These models optimize designs for both performance and cost-effective outcomes.
- Explore and Select: The software presents the array of solutions, often on a trade-off plot (e.g., cost vs. mass). The engineer can then explore the different options, analyze the trade-offs, and select the optimal design that best aligns with the project’s strategic goals. This process involves solving engineering design problems and specifically addressing complex engineering design problems to ensure the selected solution meets all requirements.
By exploring the design space using complex simulations, generative AI enables rapid evaluation of a wide range of possibilities, accelerating the path to innovative solutions.
This approach leads to parts that are not just innovative but also holistically optimized.
The case study from General Motors powerfully illustrates this. In a collaboration with Autodesk, GM engineers used generative design to reimagine a common seatbelt bracket. The AI produced over 150 design alternatives. The final selected design consolidated what was originally an eight-component assembly into a single part that was 40% lighter and 20% stronger than the original.

This has become the quintessential example of generative design’s power to simultaneously reduce complexity, cut weight, and improve performance, benefiting mechanical engineers and advancing the field of mechanical engineering.
In summary, generative AI is transforming product design & development by enabling engineers and designers to optimize designs for performance, cost, and manufacturability, while leveraging previous and existing designs, advanced simulations, and real-time feedback to solve complex engineering design problems in a cost-effective and innovative manner.
The Accelerator: How AI Driven Simulation is Supercharging Engineering
For decades, engineering simulation has been an indispensable tool, but its reliance on computationally intensive numerical methods has often relegated it to a late-stage validation role, performed by a small number of specialists.
This creates a critical bottleneck, severely limiting the number of design iterations a team can explore and stifling innovation.
AI is shattering this paradigm, transforming simulation from a bottleneck into a real-time design exploration engine. Instead of solving complex physics equations from scratch for every new design, AI models are trained on data from past simulations to learn the intricate relationships between a design’s geometry and its performance.
Once trained, these models can make nearly instantaneous predictions for new designs, significantly improving efficiency and operational efficiency.
This dramatic acceleration “democratizes” simulation, making it an accessible, interactive tool for design engineers, not just CAE specialists. AI-driven tools help reduce errors and save valuable time by automating complex analysis and streamlining workflows. The business impact is profound, enabling a level of design iteration that was previously unimaginable and directly contributing to enhanced product quality.
Comprehensive Design Exploration at Bühler Group: The industrial equipment leader needed to optimize a new food processing technology. By leveraging a cloud-native simulation platform, their teams were able to evaluate 60 distinct design variants in just two weeks.
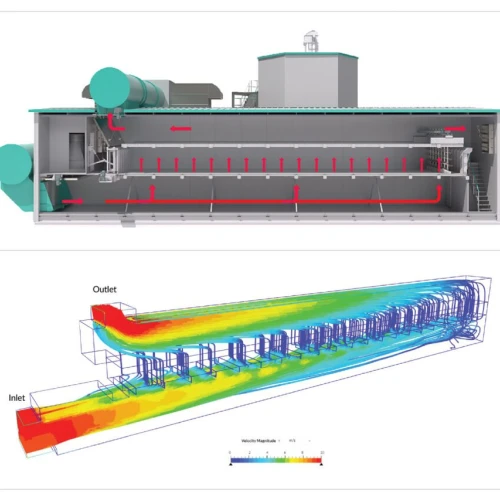
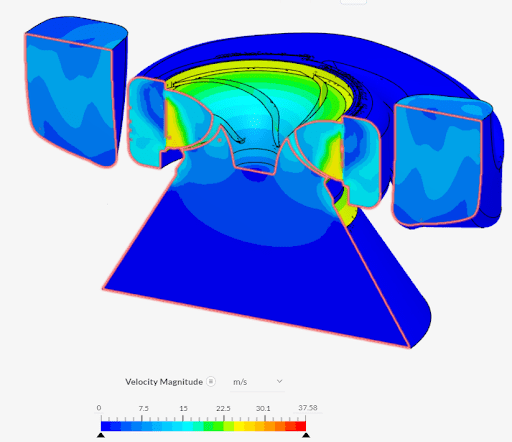
Radical Time Reduction at Hazleton Pumps: The global pump supplier traditionally relied on building and testing physical prototypes—a slow and expensive process. By adopting early-stage simulation, they achieved a staggering 99% reduction in their development timeline, compressing cycles that took months into mere days and saving time at every stage.
Simulation (SimScale) drastically changed our R&D landscape regarding time (99.9% quicker), cost (no HPC and data storage), and simulation accuracy… It allows us to complete development cycles within days instead of months, giving us a massive advantage compared to our competition. I would say that this (software) is not evolutionary but rather disruptive. Engineer, Hazleton Pumps
The Cloud-Native Imperative: The Foundation for AI at Scale
The transformative potential of AI-powered design and simulation cannot be fully realized within the constraints of legacy, on-premise computing infrastructure. A cloud-native platform is the essential foundation required to enable this new engineering paradigm.
- On-Demand Scalability: AI model training and large-scale generative design studies require immense computational power. Cloud platforms provide this massive scalability on demand, allowing teams to access supercomputing-level resources when needed and pay only for what they use, eliminating the need for costly in-house HPC hardware.
- Centralized Data: AI models are only as good as the data they are trained on. Cloud-native platforms act as a centralized hub for all critical engineering data—CAD, CAE, test data, technical documentation, and operational feedback—breaking down the information silos that cripple agility and providing the fuel for the AI engine. With all this data in one place, advanced data analytics can be applied to monitor processes, optimize operations, and drive better decision-making.
- Seamless Collaboration: The fast, iterative workflows enabled by AI demand a new level of teamwork. Cloud platforms with built-in, collaboration features are designed for this purpose, allowing globally dispersed teams to work together and concurrently on the same models, share results in real-time, and benefit from real time feedback during the product development process.
The Final Piece: Future-Proofing Your Engineering Process and Your Team
The convergence of AI and cloud-native simulation is more than a technological upgrade; it’s a strategic inflection point that will define the next generation of industry leaders. The evidence clearly shows that “companies investing in cloud-native simulation today are investing in their ability to compete tomorrow.”
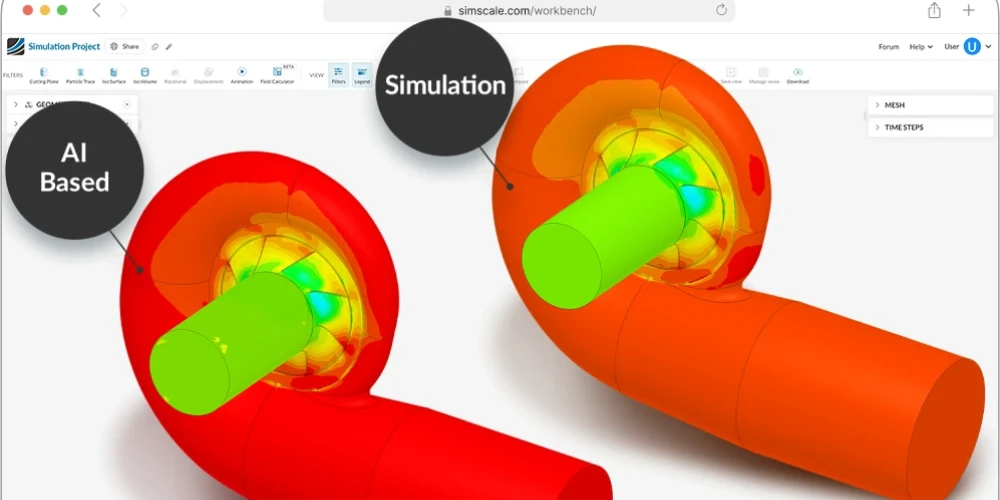
This investment is not about acquiring a static tool. It is about plugging into a platform for continuous, compounding improvement. The data feedback loops, where real-world operational data informs the next generation of designs, create a virtuous cycle. AI-driven systems can automate repetitive tasks, freeing up engineering teams to focus on innovation and strategic problem-solving. Additionally, AI helps reduce waste in production processes, supporting greater efficiency and sustainability. Early adopters will not just gain a one-time advantage; they will build an accelerating competitive lead that becomes increasingly difficult for followers to close.
For engineering leaders, the path forward is clear. The future of manufacturing will be defined by intelligence, agility, and sustainability. Embracing an AI-driven, cloud-native design platform, in collaboration with a human team, is the most critical strategic step you can take to ensure your organization is not just keeping up with the pace of change, but driving it. Looking ahead, the integration of advanced technologies like computer vision will further expand the potential of engineering applications, enabling even greater precision and efficiency.
A new global study of 300 engineering leaders reveals a widening gap between AI expectation and execution in engineering workflows, and the lessons from top performers who are closing it.