1990s Formula Car High and Low Noses Comparison
Introduction
In the early 1990s high nose designs appeared to formula 1.
Soon, most formula cars came to adopt high nose.
In this study, sevral typical nose designs during the early years of the high nose appearance were simulated to know its characteristics.
Models
Model Overview
- Flat Bottomed Floor
- Overall Width : 2150 [mm]
- Overall Length : 4440 [mm]
- Wheel Base : 2940 [mm]
Nose and Front Wing Types
Low Nose
- Low Nose
- 50 [mm] Lower Bottom Surface of Monocoque than High Nose
- Front Wing
- Horizontal
- Straight
- Fixed Directly to Nose Cone
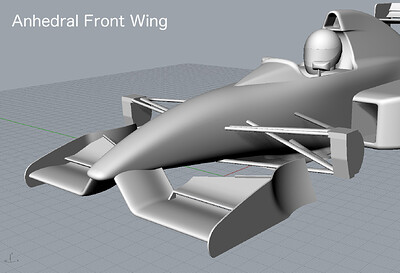
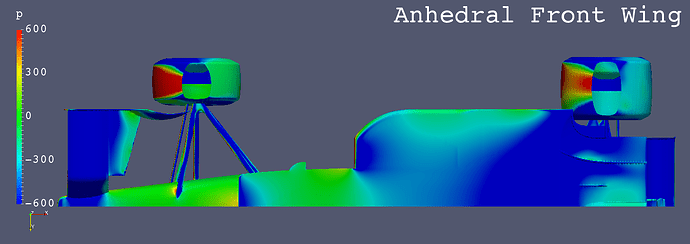
High Nose + Anhedral Front Wing
- High Nose
- Front Wing
- Anhedral
- Fixed Directly to Nose Cone
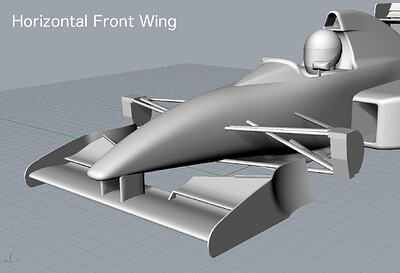
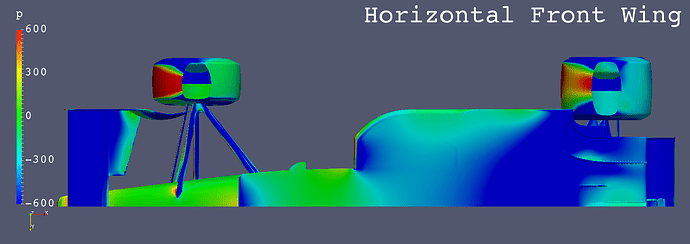
High Nose + Horizontal Front Wing
- High Nose
- Front Wing
- Horizontal
- Straight
- Fixed to Nose Cone via Vertical Stays
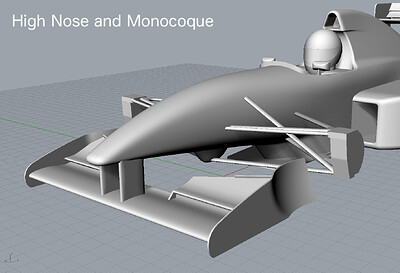
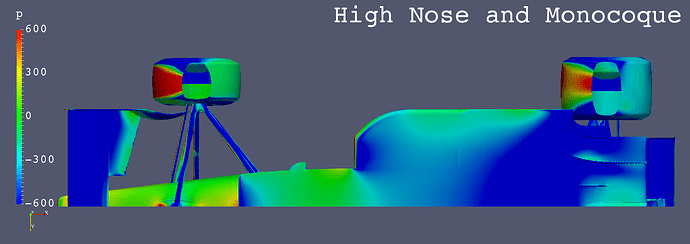
High Nose and High Monocoque
- 75 [mm] Higher Nose and Monococue
- compared with High Nose
- Front Wing
- Horizontal
- Straight
- Fixed to Nose Cone via Vertical Stays
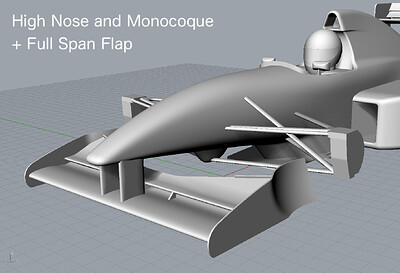
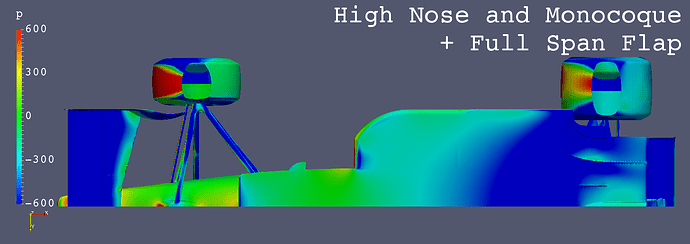
High Nose and High Monocoque + Full Span Front Flap
- Front Wing
- Horizontal
- Straight
- Fixed to Nose Cone via Vertical Stays
- Full Span Flap
- Center Flap Added
GIF Animation Comparison of the Models

Simulations
Conditions
- Freestream Velocity Magnitude Value : 40 [m/s]
- Ride Height : Front / Rear = 20 [mm] / 35 [mm]
- RF : Radiator Flow [m3/s]
Results
Low Nose
| Coef. | Whole Car | Body & Wings | Fr Wing & Nose | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9322 | 0.6169 | 0.1063 | 0.0892 | 0.0171 | 0.2744 | 0.2361 | 0.1313 | 0.1840 |
| Cl | -1.7685 | -1.9961 | -0.6532 | -0.6298 | -0.0234 | -0.6418 | -0.7011 | 0.0928 | 0.1348 |
| Clf | -0.6182 | -0.7464 | -0.8112 | -0.7823 | -0.0290 | -0.0798 | 0.1446 | 0.1073 | 0.0208 |
| Clr | -1.1503 | -1.2497 | 0.1581 | 0.1525 | 0.0056 | -0.5620 | -0.8457 | -0.0146 | 0.1140 |
| CoP | 0.6504 | 0.6261 | -0.2420 | -0.2421 | -0.2377 | 0.8756 | 1.2063 | -0.1570 | 0.8454 |
| L/D | -1.8971 | -3.2357 | -6.1424 | -7.0570 | -1.3689 | -2.3388 | -2.9689 | 0.7067 | 0.7326 |
| RF m3/s | 1.0228 |
High Nose + Anhedral Fr Wing
| Coef. | Whole Car | Body & Wings | Fr Wing & Nose | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9291 | 0.6134 | 0.0962 | 0.0866 | 0.0096 | 0.2807 | 0.2365 | 0.1318 | 0.1839 |
| Cl | -1.7557 | -1.9796 | -0.5455 | -0.5069 | -0.0386 | -0.7309 | -0.7031 | 0.0917 | 0.1321 |
| Clf | -0.5216 | -0.6487 | -0.6744 | -0.6266 | -0.0478 | -0.1193 | 0.1449 | 0.1063 | 0.0208 |
| Clr | -1.2341 | -1.3308 | 0.1289 | 0.1197 | 0.0092 | -0.6116 | -0.8481 | -0.0146 | 0.1113 |
| CoP | 0.7029 | 0.6723 | -0.2362 | -0.2361 | -0.2376 | 0.8368 | 1.2061 | -0.1595 | 0.8424 |
| L/D | -1.8896 | -3.2272 | -5.6699 | -5.8535 | -4.0166 | -2.6039 | -2.9733 | 0.6956 | 0.7185 |
| RF m3/s | 1.0411 |
High Nose + Horizontal Fr Wing
| Coef. | Whole Car | Body & Wings | Fr Wing & Nose | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9311 | 0.6157 | 0.1039 | 0.0890 | 0.0149 | 0.2757 | 0.2362 | 0.1313 | 0.1841 |
| Cl | -1.7681 | -1.9910 | -0.6064 | -0.6040 | -0.0023 | -0.6841 | -0.7005 | 0.0918 | 0.1311 |
| Clf | -0.5809 | -0.7081 | -0.7516 | -0.7499 | -0.0017 | -0.1011 | 0.1446 | 0.1064 | 0.0208 |
| Clr | -1.1872 | -1.2829 | 0.1452 | 0.1458 | -0.0006 | -0.5830 | -0.8451 | -0.0146 | 0.1103 |
| CoP | 0.6715 | 0.6443 | -0.2395 | -0.2414 | 0.2569 | 0.8522 | 1.2064 | -0.1587 | 0.8410 |
| L/D | -1.8989 | -3.2336 | -5.8388 | -6.7886 | -0.1575 | -2.4813 | -2.9662 | 0.6993 | 0.7122 |
| RF m3/s | 1.0297 |
High Nose and Monocoque
| Coef. | Whole Car | Body & Wings | Fr Wing & Nose | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9412 | 0.6229 | 0.1050 | 0.0886 | 0.0164 | 0.2834 | 0.2345 | 0.1309 | 0.1875 |
| Cl | -1.7754 | -2.0004 | -0.5961 | -0.5981 | 0.0020 | -0.7044 | -0.6998 | 0.0901 | 0.1348 |
| Clf | -0.5749 | -0.7007 | -0.7385 | -0.7424 | 0.0039 | -0.1062 | 0.1440 | 0.1046 | 0.0212 |
| Clr | -1.2006 | -1.2996 | 0.1424 | 0.1443 | -0.0019 | -0.5982 | -0.8438 | -0.0145 | 0.1136 |
| CoP | 0.6762 | 0.6497 | -0.2389 | -0.2413 | -0.9543 | 0.8492 | 1.2057 | -0.1612 | 0.8426 |
| L/D | -1.8863 | -3.2115 | -5.6783 | -6.7542 | 0.1215 | -2.4860 | -2.9837 | 0.6884 | 0.7192 |
| RF m3/s | 1.0420 |
High Nose and Monocoque + Full Span Flap
| Coef. | Whole Car | Body & Wings | Fr Wing & Nose | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9476 | 0.6288 | 0.1260 | 0.1092 | 0.0169 | 0.2690 | 0.2338 | 0.1303 | 0.1885 |
| Cl | -1.8414 | -2.0692 | -0.8068 | -0.8181 | 0.0113 | -0.5712 | -0.6912 | 0.0902 | 0.1377 |
| Clf | -0.7764 | -0.9024 | -1.0018 | -1.0172 | 0.0154 | -0.0435 | 0.1429 | 0.1046 | 0.0213 |
| Clr | -1.0650 | -1.1668 | 0.1950 | 0.1991 | -0.0041 | -0.5277 | -0.8342 | -0.0145 | 0.1163 |
| CoP | 0.5783 | 0.5639 | -0.2417 | -0.2434 | -0.3657 | 0.9238 | 1.2068 | -0.1603 | 0.8450 |
| L/D | -1.9431 | -3.2906 | -6.4020 | -7.4945 | 0.6683 | -2.1234 | -2.9565 | 0.6920 | 0.7302 |
| RF m3/s | 0.9741 |
Comparisons
Whole Body Coefficients Comparison
Whole Body Coefficients
| Coef. | Low Nose | Anhedral Fr Wing |
Horizontal Fr Wing |
High Monocoque | High Monocoque + Full Flap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9322 | 0.9291 | 0.9311 | 0.9412 | 0.9476 |
| Cl | -1.7685 | -1.7557 | -1.7681 | -1.7754 | -1.8414 |
| Clf | -0.6182 | -0.5216 | -0.5809 | -0.5749 | -0.7764 |
| Clr | -1.1503 | -1.2341 | -1.1872 | -1.2006 | -1.0650 |
| CoP | 0.6504 | 0.7029 | 0.6715 | 0.6762 | 0.5783 |
| L/D | -1.8971 | -1.8896 | -1.8989 | -1.8863 | -1.9431 |
| RF m3/s | 1.0228 | 1.0411 | 1.0297 | 1.0420 | 0.9741 |
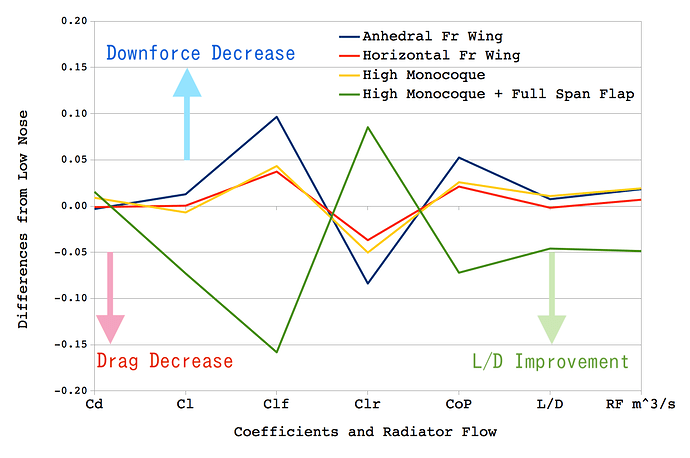
Whole Body Coefficient Differences
- Control : Low Nose
| Coef. | Low Nose | Anhedral Fr Wing |
Horizontal Fr Wing |
High Monocoque | High Monocoque + Full Flap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.0000 | -0.0031 | -0.0011 | 0.0090 | 0.0155 |
| Cl | 0.0000 | 0.0128 | 0.0004 | -0.0070 | -0.0729 |
| Clf | 0.0000 | 0.0966 | 0.0373 | 0.0433 | -0.1582 |
| Clr | 0.0000 | -0.0839 | -0.0369 | -0.0503 | 0.0853 |
| CoP | 0.0000 | 0.0525 | 0.0210 | 0.0258 | -0.0721 |
| L/D | 0.0000 | 0.0075 | -0.0017 | 0.0108 | -0.0460 |
| RF m3/s | 0.0000 | 0.0183 | 0.0069 | 0.0193 | -0.0486 |
- The drags (Cd) and the downforce total amounts (Cl) of “Anhedral Fr Wing”, “Horizontal Fr Wing” and “High Monocoque” are not different much with that of “Low Nose”.
- The downforce distributions (Clf,Clr,CoP) of “Anhedral Fr Wing”, “Horizontal Fr Wing” and “High Monocoque” shift to the rear at each rate.
- The shift of “Anhedral Fr Wing” is the largest.
- “Full Span Flap” greatly increases the front down force (Clf).
- On the other hand, the rear down force (Clr) is greatly reduced.
- L/D is improved, but it is common to improve when downforce increases, so it is necessary to evaluate after conditioning such as distribution.
Cl of Each Part Comparison
Cl Comparison
| Types | Whole Car | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Nose | -1.7685 | -0.6298 | -0.0234 | -0.6418 | -0.7011 | 0.0928 | 0.1348 |
| Anhedral Fr Wing |
-1.7557 | -0.5069 | -0.0386 | -0.7309 | -0.7031 | 0.0917 | 0.1321 |
| Horizontal Fr Wing |
-1.7681 | -0.6040 | -0.0023 | -0.6841 | -0.7005 | 0.0918 | 0.1311 |
| High Monocoque | -1.7754 | -0.5981 | 0.0020 | -0.7044 | -0.6998 | 0.0901 | 0.1348 |
| High Monocoque + Full Span Flap |
-1.8414 | -0.8181 | 0.0113 | -0.5712 | -0.6912 | 0.0902 | 0.1377 |
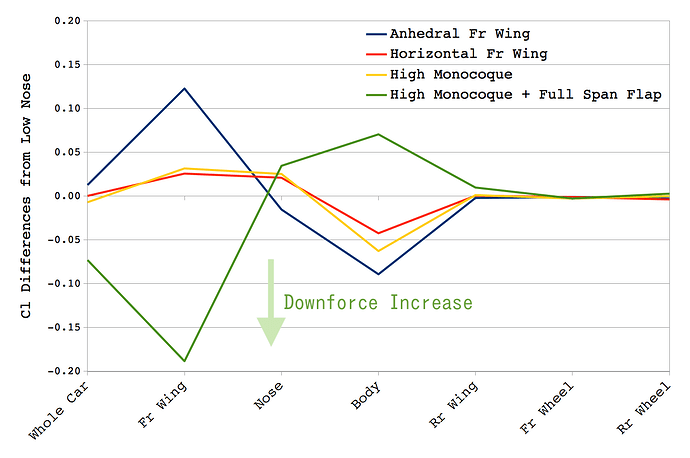
Cl Differences Comparison
- Control : Low Nose
| Types | Whole Car | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Nose | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Anhedral Fr Wing |
0.0128 | 0.1229 | -0.0152 | -0.0891 | -0.0020 | -0.0011 | -0.0027 |
| Horizontal Fr Wing |
0.0004 | 0.0257 | 0.0211 | -0.0423 | 0.0006 | -0.0010 | -0.0037 |
| High Monocoque | -0.0070 | 0.0316 | 0.0254 | -0.0626 | 0.0013 | -0.0027 | 0.0000 |
| High Monocoque + Full Span Flap |
-0.0729 | -0.1883 | 0.0347 | 0.0706 | 0.0099 | -0.0026 | 0.0028 |
- The “Fr Wing” downforces of “Anhedral Fr Wing”, “Horizontal Fr Wing” and “High Monocoque” decrease.
- The “Body” downforces of “Anhedral Fr Wing”, “Horizontal Fr Wing” and “High Monocoque” increase.
- “Full Span Flap” (Center Flap) increases “Fr Wing” downforce but significantly decreases “Body” downforce.
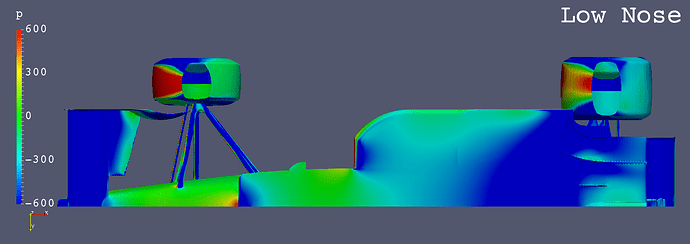
Pressure Comparison
Bottom Surfaces Pressure Comparison
GIF Animation of Bottom Surfaces Pressure Comparison
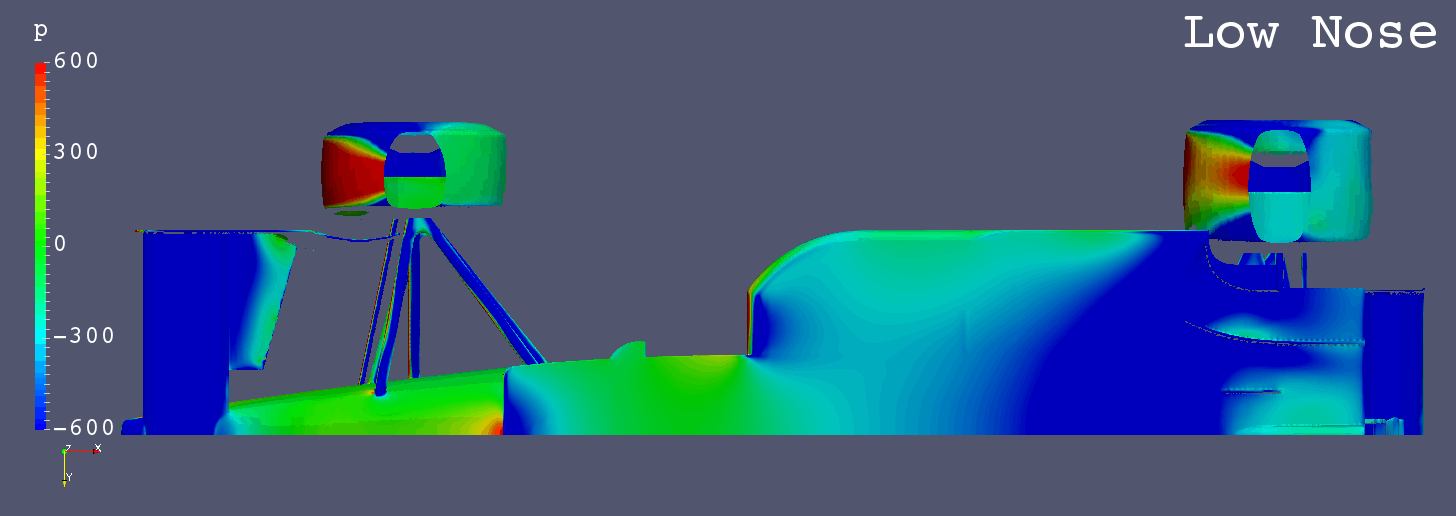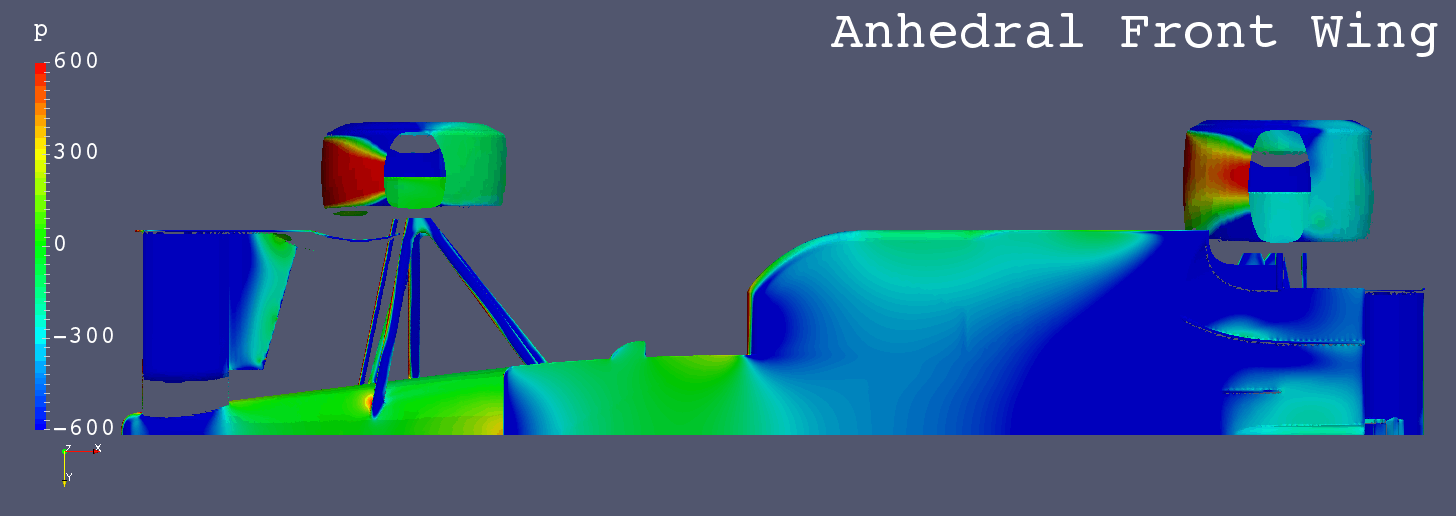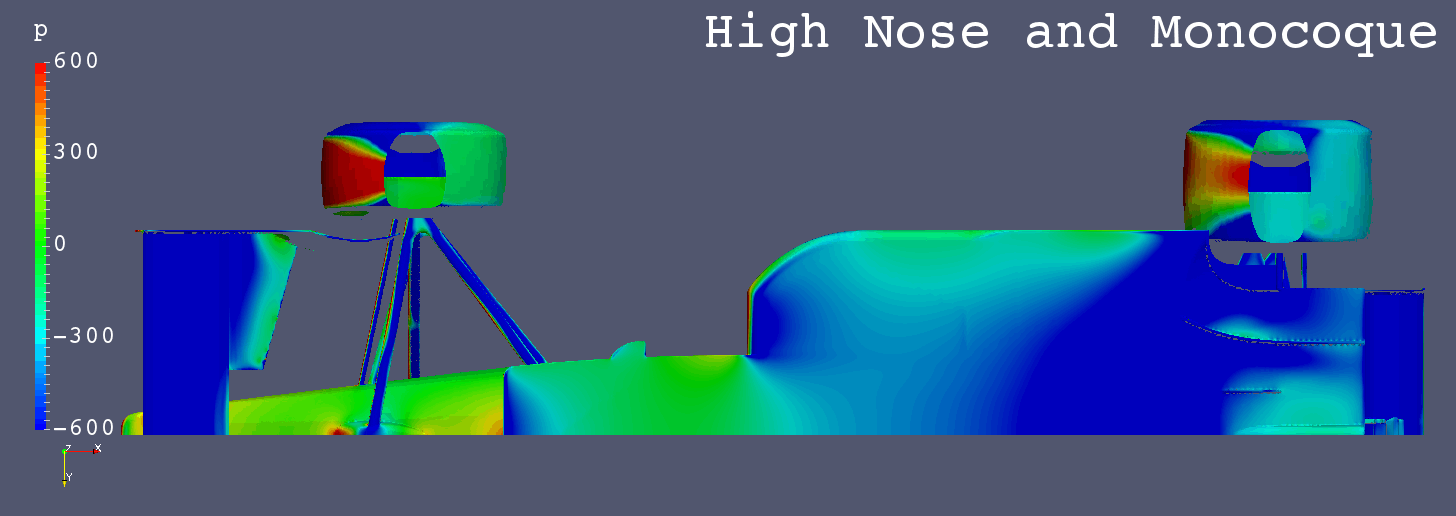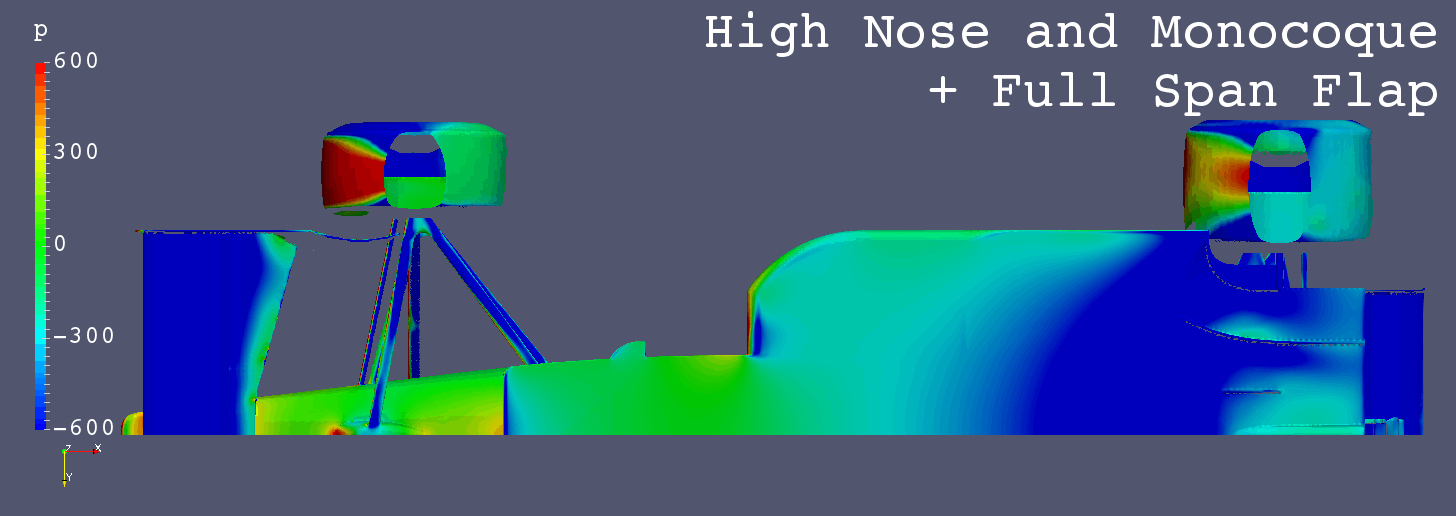
Each Still Images
- The low pressure areas below the floors of “Anhedral Fr Wing”, “Horizontal Fr Wing” and “High Monocoque” are larger than “Low Nose”.
- “High Nose” causes more air flow below the floor.
- “Full Span Flap” (Center Flap) greatly decreases the low pressure area on the floor from “High Nose and Monocoque” only.
- It is inferred that the amount of air flow in the area from the nose to the center of the front wing influences the amount of air flow below the floor.
Pressure Comparison Front-Left View
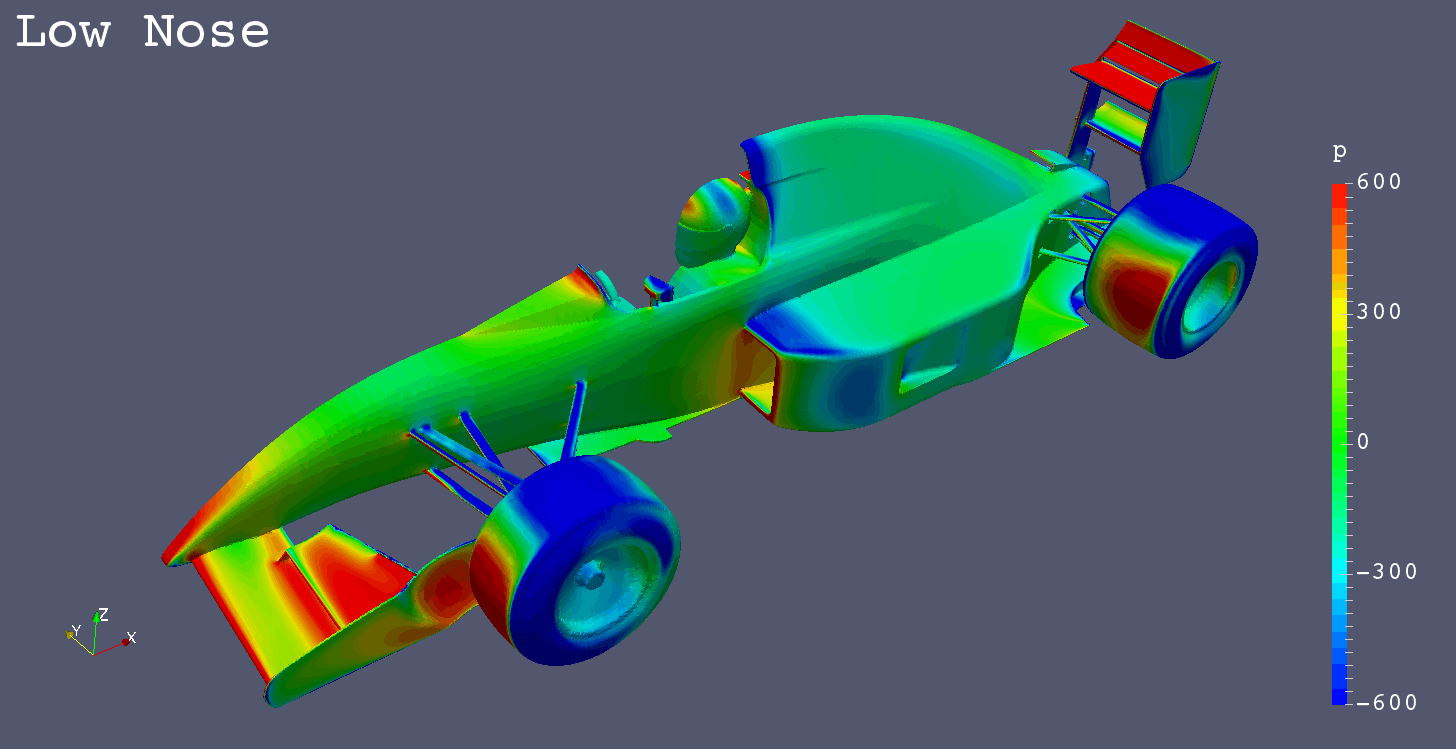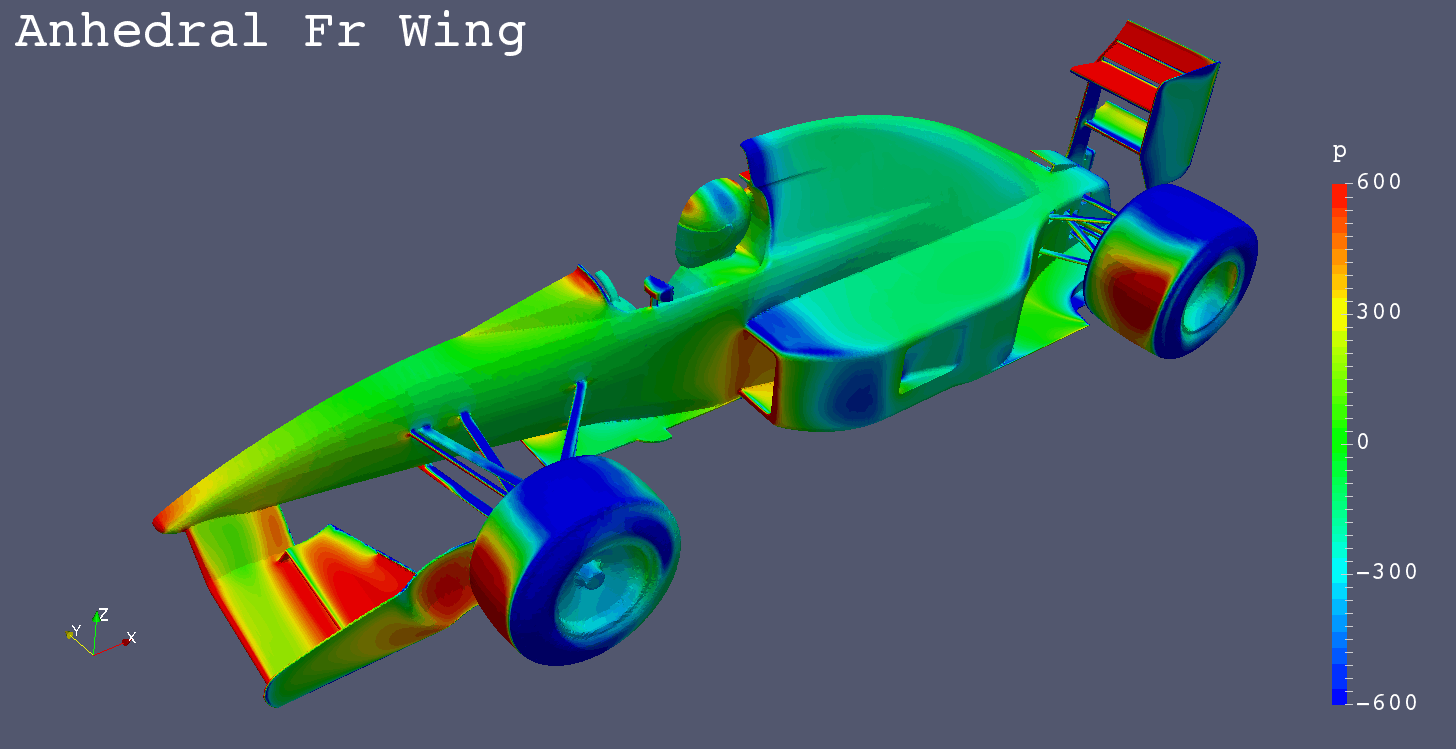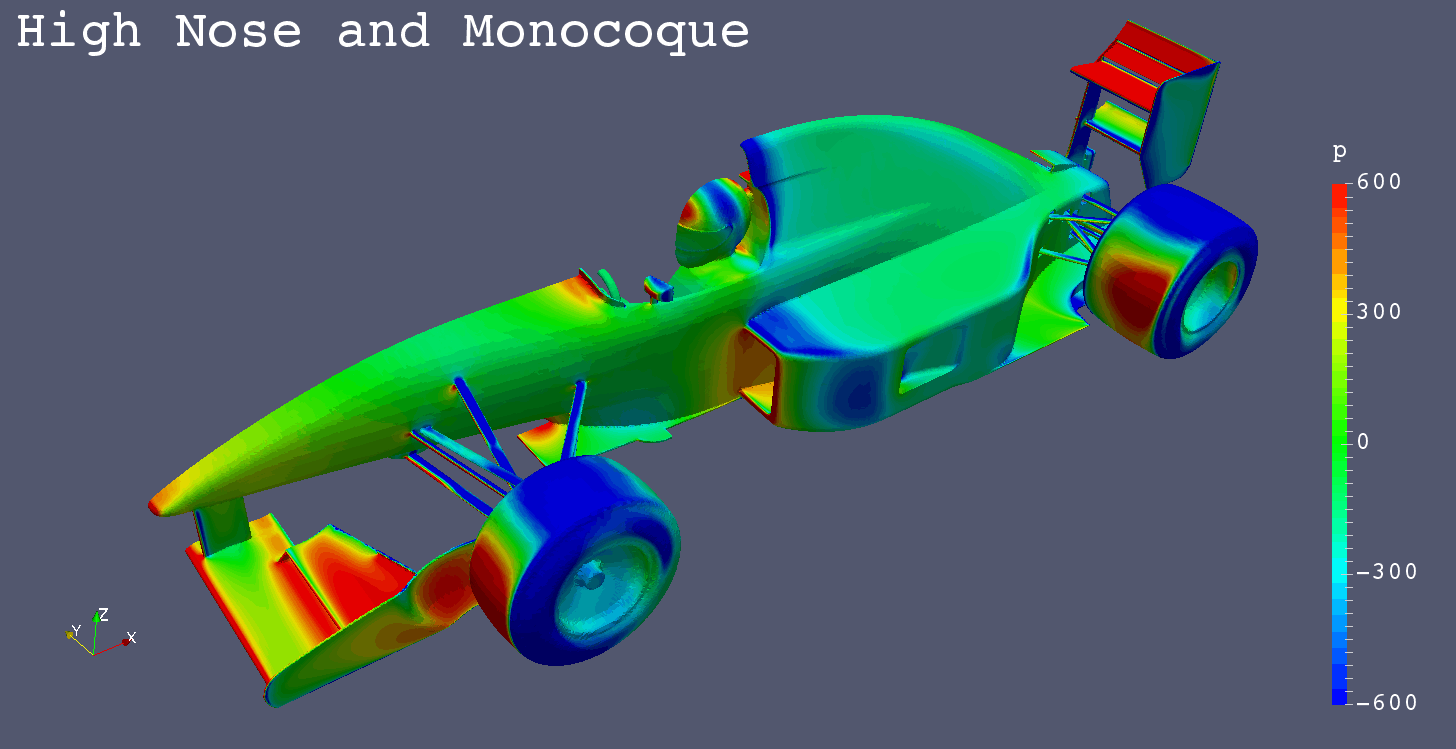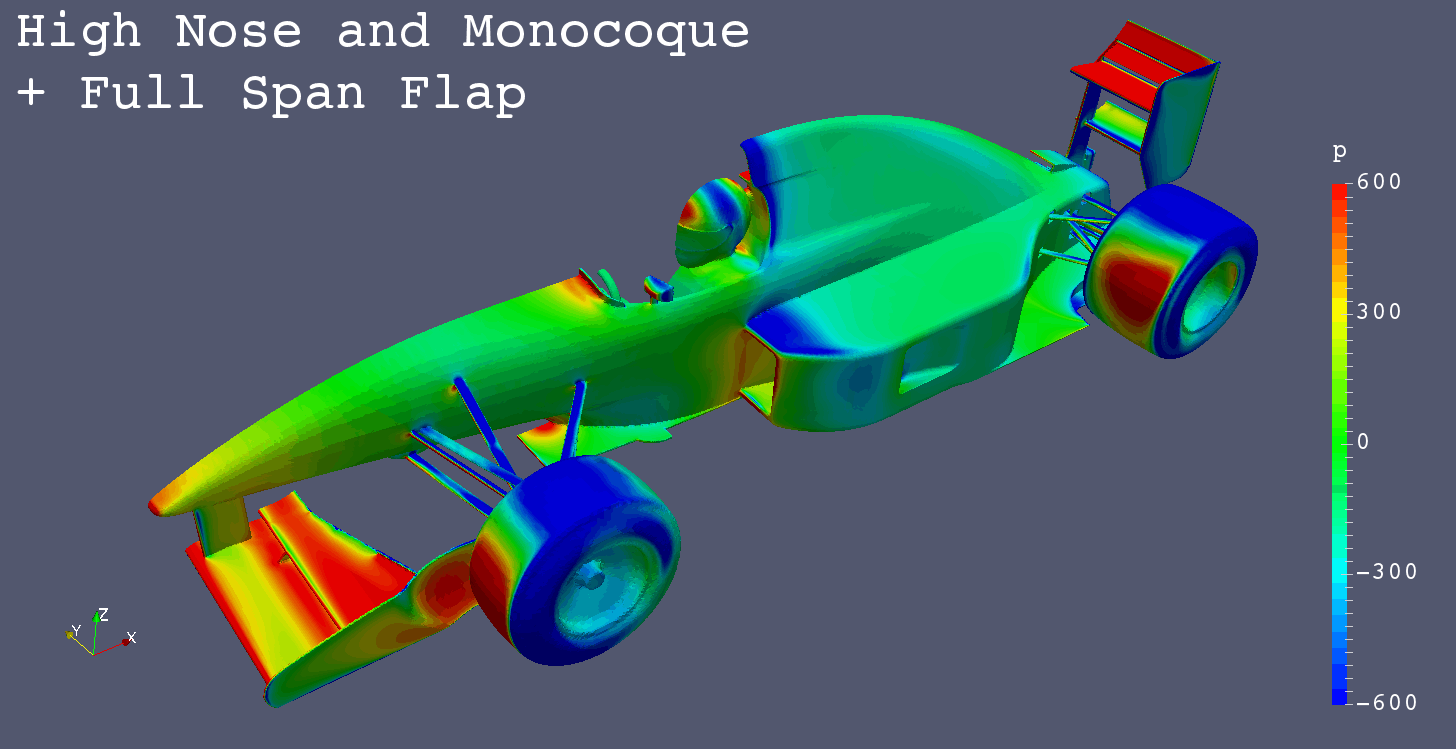
Summary
- The drags (Cd) and the downforce total amounts (Cl) of “High Noses” are not different much with that of “Low Nose”.
- The downforce distributions (Clf,Clr,CoP) of “High Noses” shift to the rear at each rate.
- The “Fr Wing” downforces of “High Noses” decrease.
- The “Body” downforces of “High Noses” increase.
- The low pressure areas below the floors of “High Noses” are larger than “Low Nose”.
- “High Nose” causes more air flow below the floor.
- “Full Span Flap” (Center Flap) greatly increases the front down force (Clf), but the rear down force (Clr) is greatly reduced.
- “Full Span Flap” greatly decreases the low pressure area on the floor bottom from “High Nose and Monocoque” only.
- It is inferred that the amount of air flow in the area from the nose to the center of the front wing influences the amount of air flow below the floor.