I created a new simulation project called '1990s F1 High and Low Noses':
1990s F1 High and Low Noses CFD Simulations
More of my public projects can be found here.
I created a new simulation project called '1990s F1 High and Low Noses':
1990s F1 High and Low Noses CFD Simulations
More of my public projects can be found here.
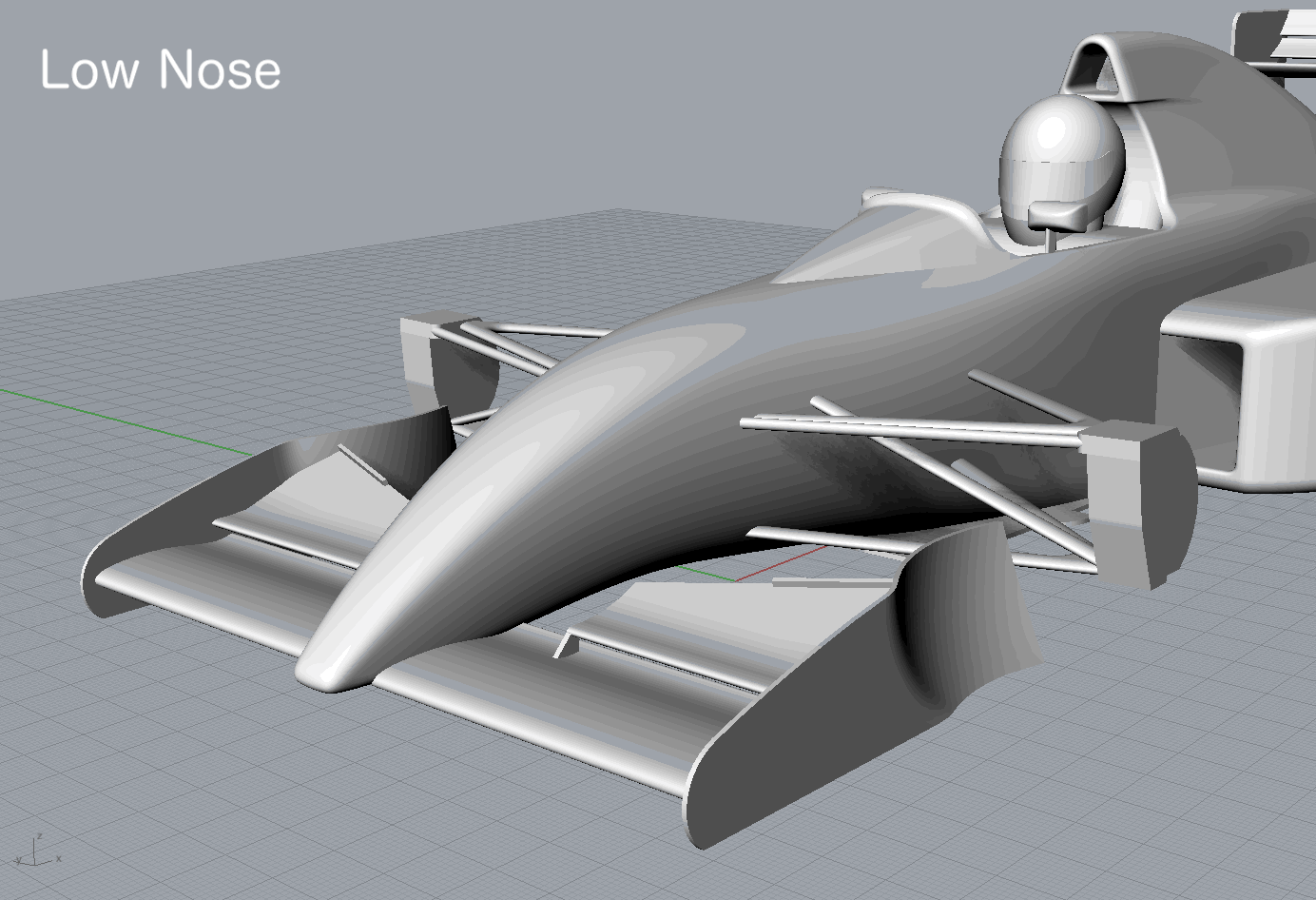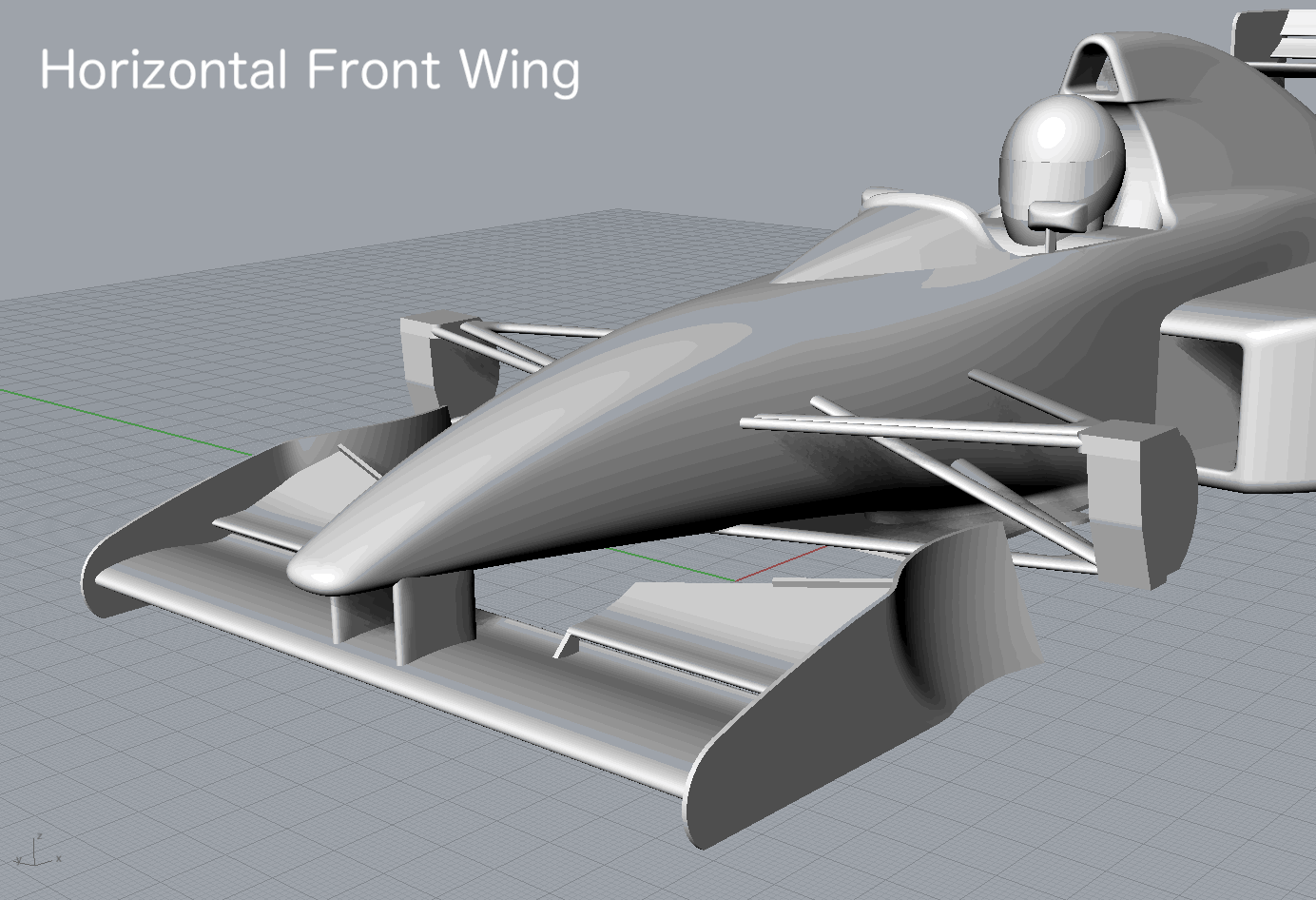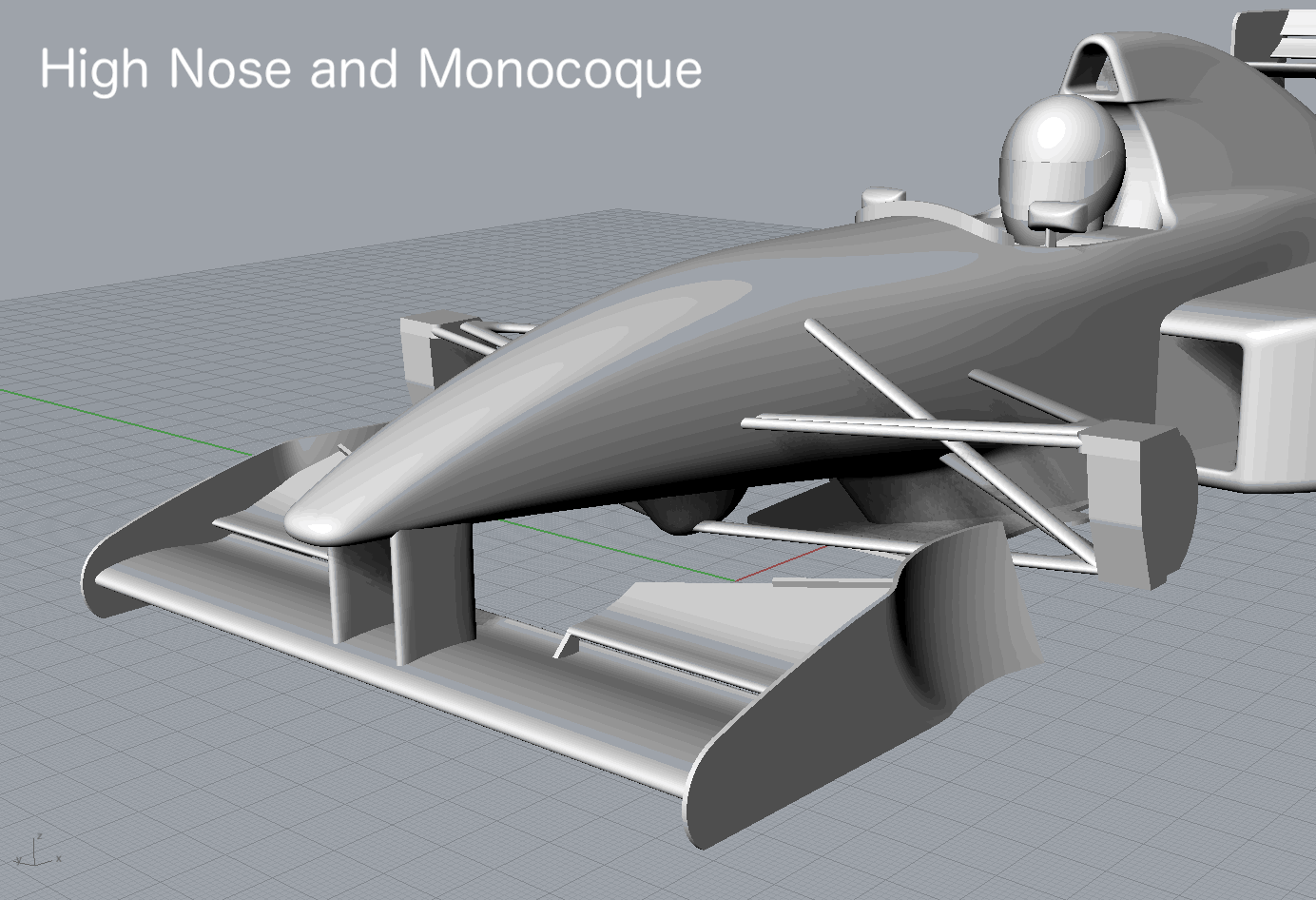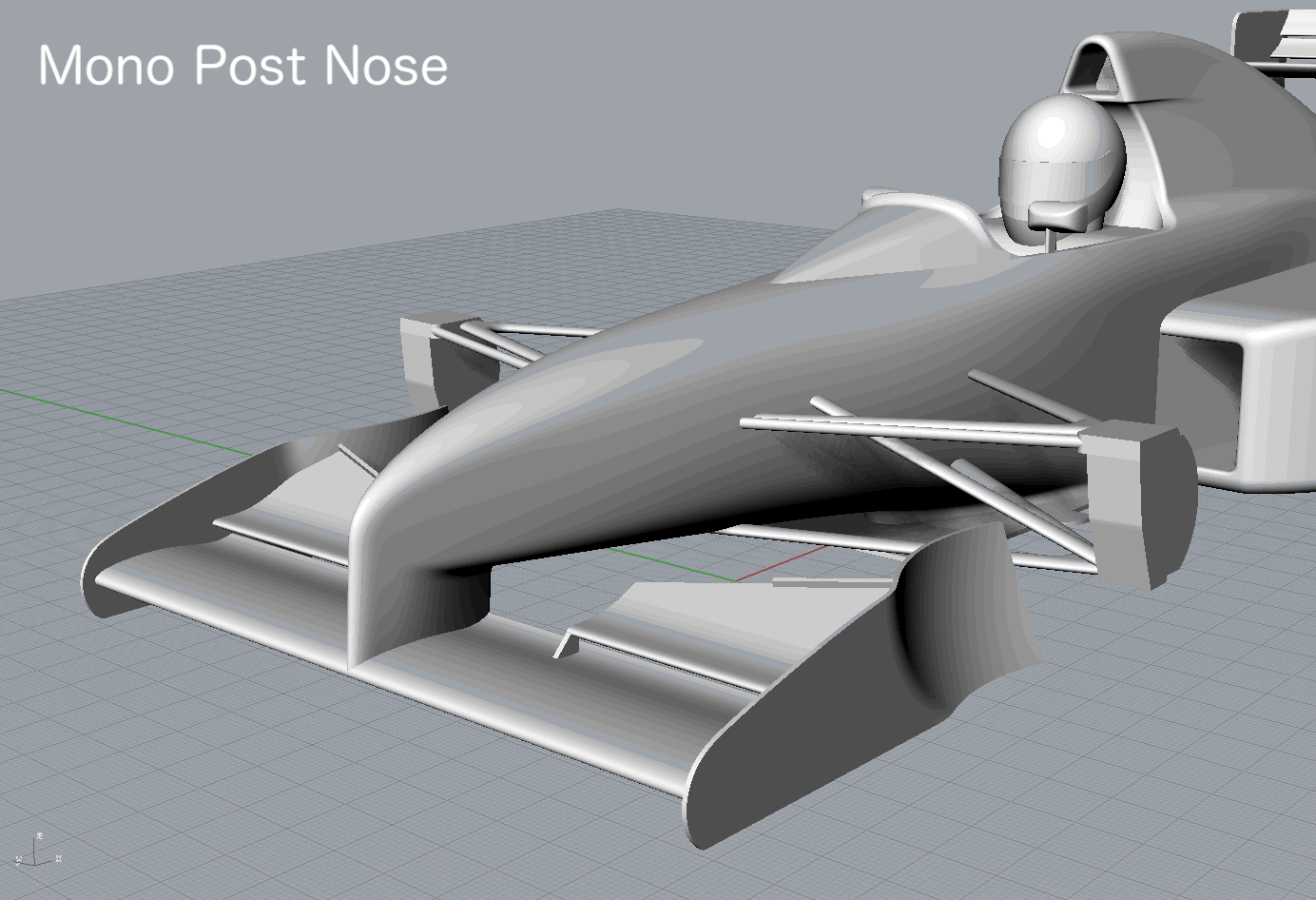
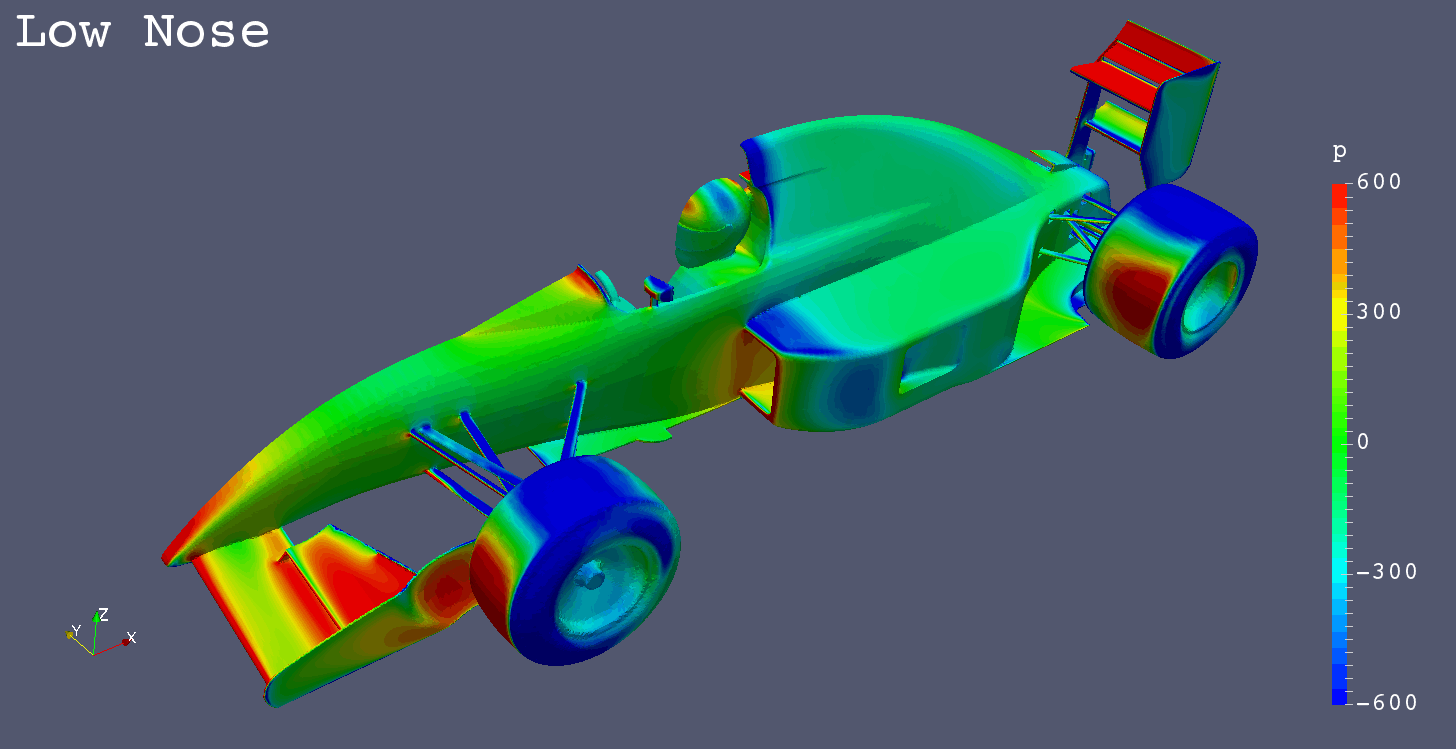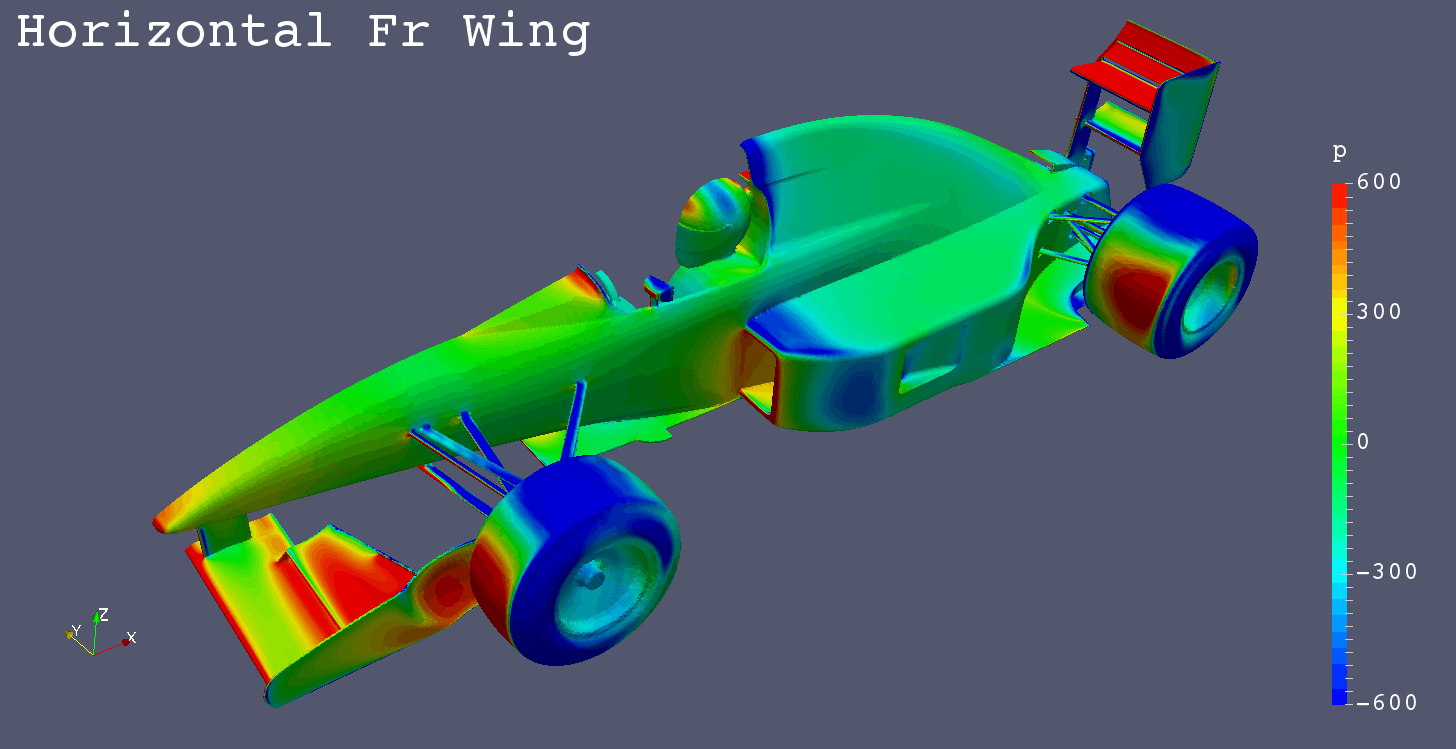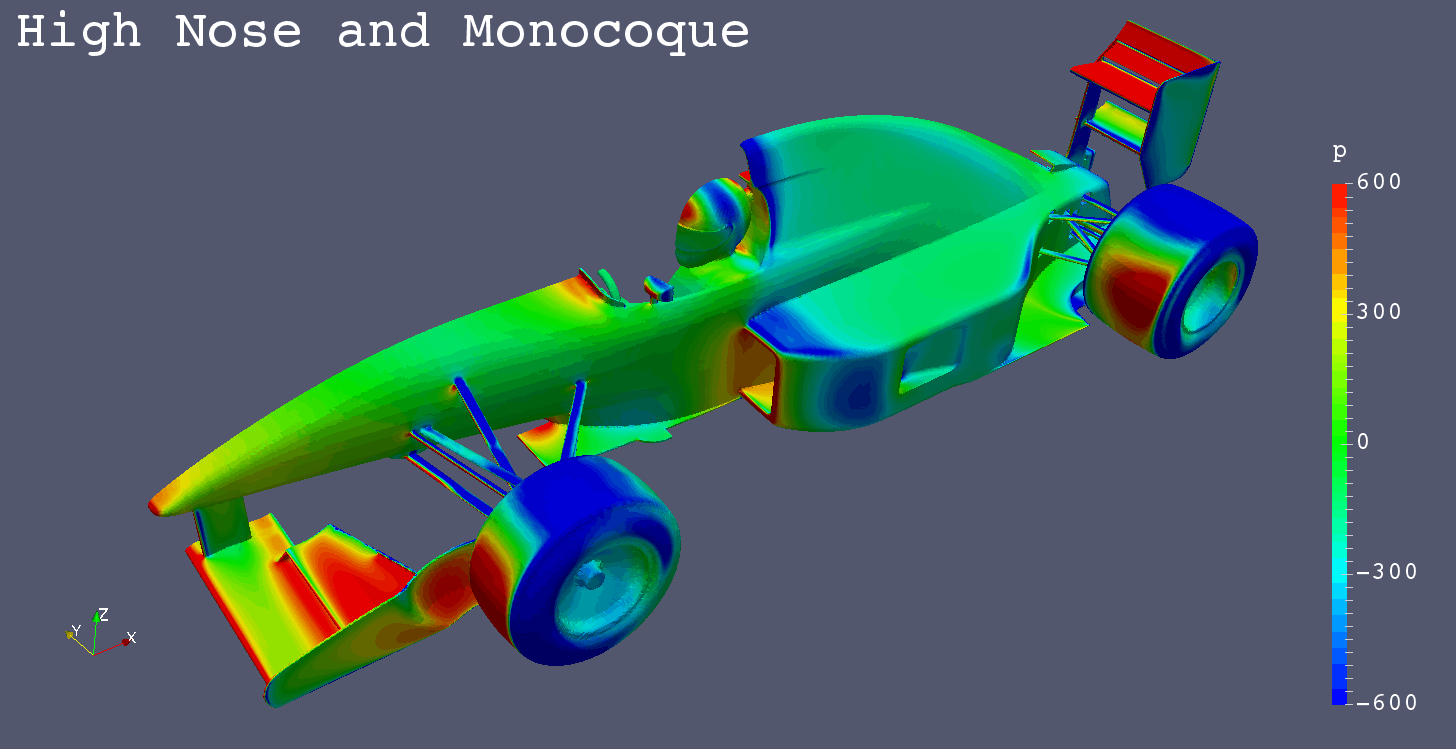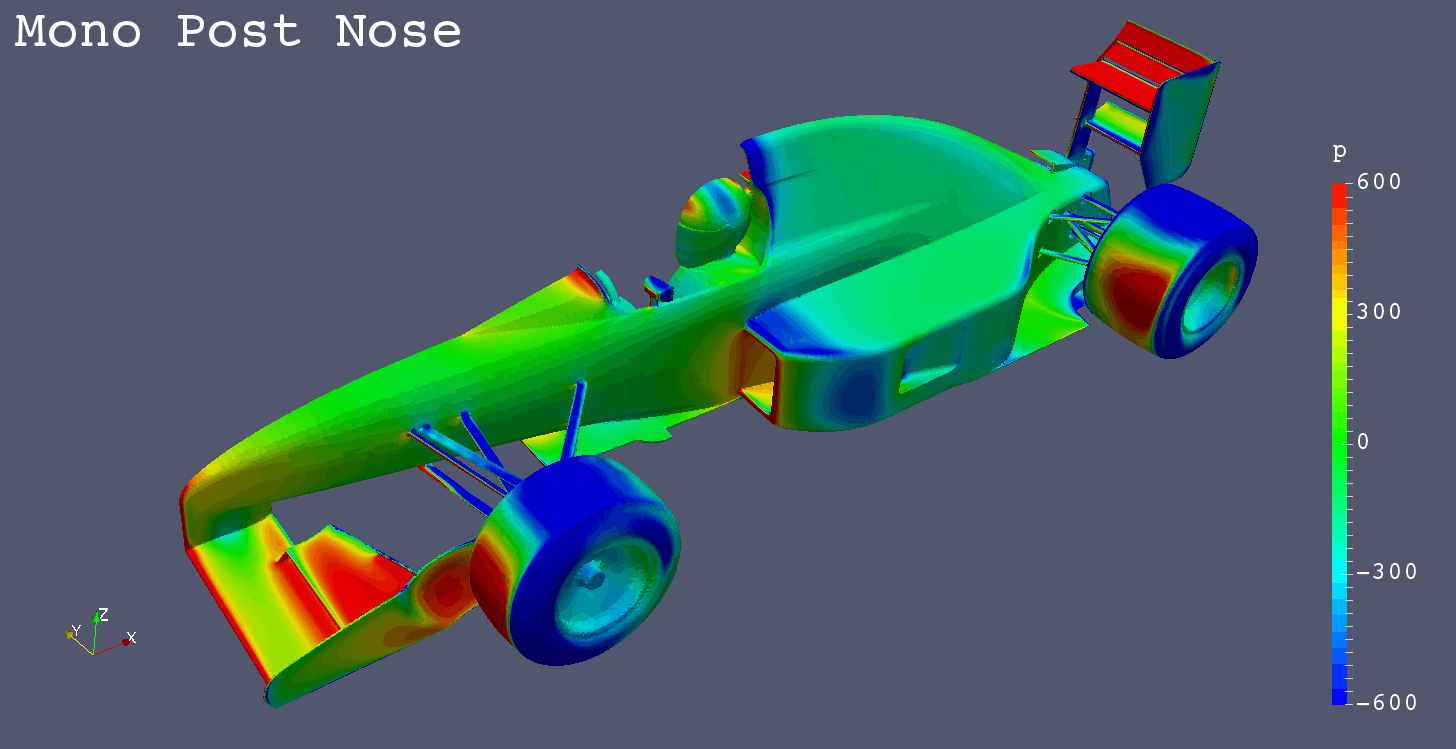
In the early 1990s high nose designs appeared to formula 1.
Soon, most formula cars came to adopt high nose.
In this study, sevral typical nose designs during the early years of the high nose appearance were simulated to know its characteristics.

| Coef. | Whole Car | Body & Wings | Fr Wing & Nose | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9322 | 0.6169 | 0.1063 | 0.0892 | 0.0171 | 0.2744 | 0.2361 | 0.1313 | 0.1840 |
| Cl | -1.7685 | -1.9961 | -0.6532 | -0.6298 | -0.0234 | -0.6418 | -0.7011 | 0.0928 | 0.1348 |
| Clf | -0.6182 | -0.7464 | -0.8112 | -0.7823 | -0.0290 | -0.0798 | 0.1446 | 0.1073 | 0.0208 |
| Clr | -1.1503 | -1.2497 | 0.1581 | 0.1525 | 0.0056 | -0.5620 | -0.8457 | -0.0146 | 0.1140 |
| CoP | 0.6504 | 0.6261 | -0.2420 | -0.2421 | -0.2377 | 0.8756 | 1.2063 | -0.1570 | 0.8454 |
| L/D | -1.8971 | -3.2357 | -6.1424 | -7.0570 | -1.3689 | -2.3388 | -2.9689 | 0.7067 | 0.7326 |
| RF m3/s | 1.0228 |
| Coef. | Whole Car | Body & Wings | Fr Wing & Nose | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9291 | 0.6134 | 0.0962 | 0.0866 | 0.0096 | 0.2807 | 0.2365 | 0.1318 | 0.1839 |
| Cl | -1.7557 | -1.9796 | -0.5455 | -0.5069 | -0.0386 | -0.7309 | -0.7031 | 0.0917 | 0.1321 |
| Clf | -0.5216 | -0.6487 | -0.6744 | -0.6266 | -0.0478 | -0.1193 | 0.1449 | 0.1063 | 0.0208 |
| Clr | -1.2341 | -1.3308 | 0.1289 | 0.1197 | 0.0092 | -0.6116 | -0.8481 | -0.0146 | 0.1113 |
| CoP | 0.7029 | 0.6723 | -0.2362 | -0.2361 | -0.2376 | 0.8368 | 1.2061 | -0.1595 | 0.8424 |
| L/D | -1.8896 | -3.2272 | -5.6699 | -5.8535 | -4.0166 | -2.6039 | -2.9733 | 0.6956 | 0.7185 |
| RF m3/s | 1.0411 |
| Coef. | Whole Car | Body & Wings | Fr Wing & Nose | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9311 | 0.6157 | 0.1039 | 0.0890 | 0.0149 | 0.2757 | 0.2362 | 0.1313 | 0.1841 |
| Cl | -1.7681 | -1.9910 | -0.6064 | -0.6040 | -0.0023 | -0.6841 | -0.7005 | 0.0918 | 0.1311 |
| Clf | -0.5809 | -0.7081 | -0.7516 | -0.7499 | -0.0017 | -0.1011 | 0.1446 | 0.1064 | 0.0208 |
| Clr | -1.1872 | -1.2829 | 0.1452 | 0.1458 | -0.0006 | -0.5830 | -0.8451 | -0.0146 | 0.1103 |
| CoP | 0.6715 | 0.6443 | -0.2395 | -0.2414 | 0.2569 | 0.8522 | 1.2064 | -0.1587 | 0.8410 |
| L/D | -1.8989 | -3.2336 | -5.8388 | -6.7886 | -0.1575 | -2.4813 | -2.9662 | 0.6993 | 0.7122 |
| RF m3/s | 1.0297 |
| Coef. | Whole Car | Body & Wings | Fr Wing & Nose | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9412 | 0.6229 | 0.1050 | 0.0886 | 0.0164 | 0.2834 | 0.2345 | 0.1309 | 0.1875 |
| Cl | -1.7754 | -2.0004 | -0.5961 | -0.5981 | 0.0020 | -0.7044 | -0.6998 | 0.0901 | 0.1348 |
| Clf | -0.5749 | -0.7007 | -0.7385 | -0.7424 | 0.0039 | -0.1062 | 0.1440 | 0.1046 | 0.0212 |
| Clr | -1.2006 | -1.2996 | 0.1424 | 0.1443 | -0.0019 | -0.5982 | -0.8438 | -0.0145 | 0.1136 |
| CoP | 0.6762 | 0.6497 | -0.2389 | -0.2413 | -0.9543 | 0.8492 | 1.2057 | -0.1612 | 0.8426 |
| L/D | -1.8863 | -3.2115 | -5.6783 | -6.7542 | 0.1215 | -2.4860 | -2.9837 | 0.6884 | 0.7192 |
| RF m3/s | 1.0420 |
| Coef. | Whole Car | Body & Wings | Fr Wing & Nose | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9476 | 0.6288 | 0.1260 | 0.1092 | 0.0169 | 0.2690 | 0.2338 | 0.1303 | 0.1885 |
| Cl | -1.8414 | -2.0692 | -0.8068 | -0.8181 | 0.0113 | -0.5712 | -0.6912 | 0.0902 | 0.1377 |
| Clf | -0.7764 | -0.9024 | -1.0018 | -1.0172 | 0.0154 | -0.0435 | 0.1429 | 0.1046 | 0.0213 |
| Clr | -1.0650 | -1.1668 | 0.1950 | 0.1991 | -0.0041 | -0.5277 | -0.8342 | -0.0145 | 0.1163 |
| CoP | 0.5783 | 0.5639 | -0.2417 | -0.2434 | -0.3657 | 0.9238 | 1.2068 | -0.1603 | 0.8450 |
| L/D | -1.9431 | -3.2906 | -6.4020 | -7.4945 | 0.6683 | -2.1234 | -2.9565 | 0.6920 | 0.7302 |
| RF m3/s | 0.9741 |
| Coef. | Low Nose | Anhedral Fr Wing |
Horizontal Fr Wing |
High Monocoque | High Monocoque + Full Flap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9322 | 0.9291 | 0.9311 | 0.9412 | 0.9476 |
| Cl | -1.7685 | -1.7557 | -1.7681 | -1.7754 | -1.8414 |
| Clf | -0.6182 | -0.5216 | -0.5809 | -0.5749 | -0.7764 |
| Clr | -1.1503 | -1.2341 | -1.1872 | -1.2006 | -1.0650 |
| CoP | 0.6504 | 0.7029 | 0.6715 | 0.6762 | 0.5783 |
| L/D | -1.8971 | -1.8896 | -1.8989 | -1.8863 | -1.9431 |
| RF m3/s | 1.0228 | 1.0411 | 1.0297 | 1.0420 | 0.9741 |
| Coef. | Low Nose | Anhedral Fr Wing |
Horizontal Fr Wing |
High Monocoque | High Monocoque + Full Flap |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.0000 | -0.0031 | -0.0011 | 0.0090 | 0.0155 |
| Cl | 0.0000 | 0.0128 | 0.0004 | -0.0070 | -0.0729 |
| Clf | 0.0000 | 0.0966 | 0.0373 | 0.0433 | -0.1582 |
| Clr | 0.0000 | -0.0839 | -0.0369 | -0.0503 | 0.0853 |
| CoP | 0.0000 | 0.0525 | 0.0210 | 0.0258 | -0.0721 |
| L/D | 0.0000 | 0.0075 | -0.0017 | 0.0108 | -0.0460 |
| RF m3/s | 0.0000 | 0.0183 | 0.0069 | 0.0193 | -0.0486 |
| Types | Whole Car | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Nose | -1.7685 | -0.6298 | -0.0234 | -0.6418 | -0.7011 | 0.0928 | 0.1348 |
| Anhedral Fr Wing |
-1.7557 | -0.5069 | -0.0386 | -0.7309 | -0.7031 | 0.0917 | 0.1321 |
| Horizontal Fr Wing |
-1.7681 | -0.6040 | -0.0023 | -0.6841 | -0.7005 | 0.0918 | 0.1311 |
| High Monocoque | -1.7754 | -0.5981 | 0.0020 | -0.7044 | -0.6998 | 0.0901 | 0.1348 |
| High Monocoque + Full Span Flap |
-1.8414 | -0.8181 | 0.0113 | -0.5712 | -0.6912 | 0.0902 | 0.1377 |
| Types | Whole Car | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Nose | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Anhedral Fr Wing |
0.0128 | 0.1229 | -0.0152 | -0.0891 | -0.0020 | -0.0011 | -0.0027 |
| Horizontal Fr Wing |
0.0004 | 0.0257 | 0.0211 | -0.0423 | 0.0006 | -0.0010 | -0.0037 |
| High Monocoque | -0.0070 | 0.0316 | 0.0254 | -0.0626 | 0.0013 | -0.0027 | 0.0000 |
| High Monocoque + Full Span Flap |
-0.0729 | -0.1883 | 0.0347 | 0.0706 | 0.0099 | -0.0026 | 0.0028 |
GIF Animation of Bottom Surfaces Pressure Comparison
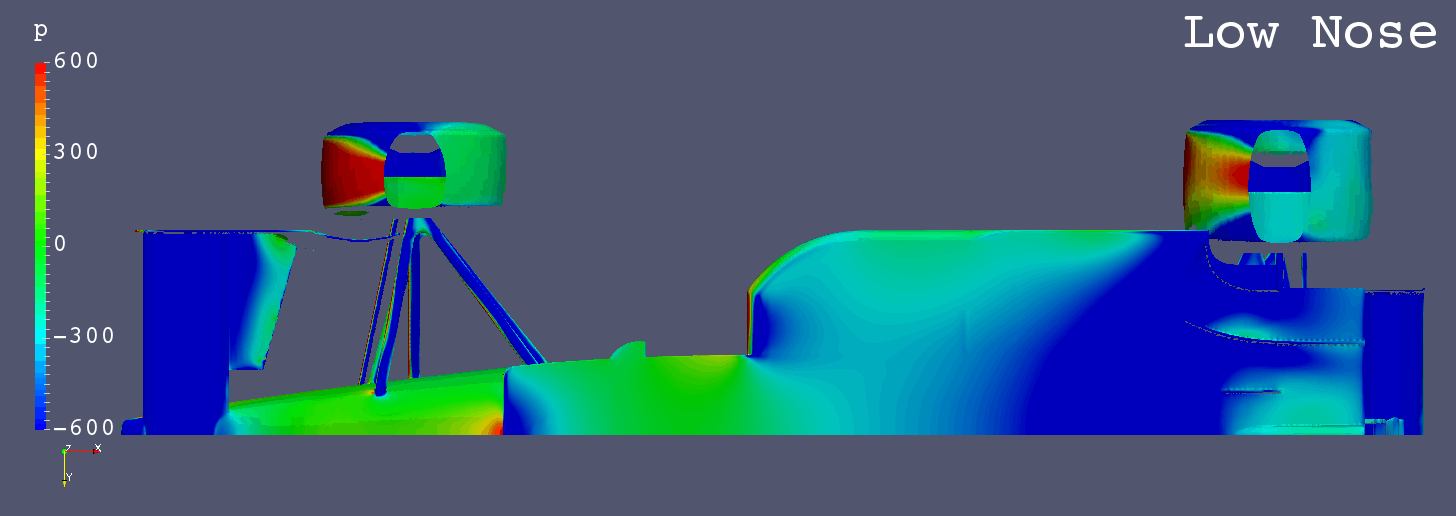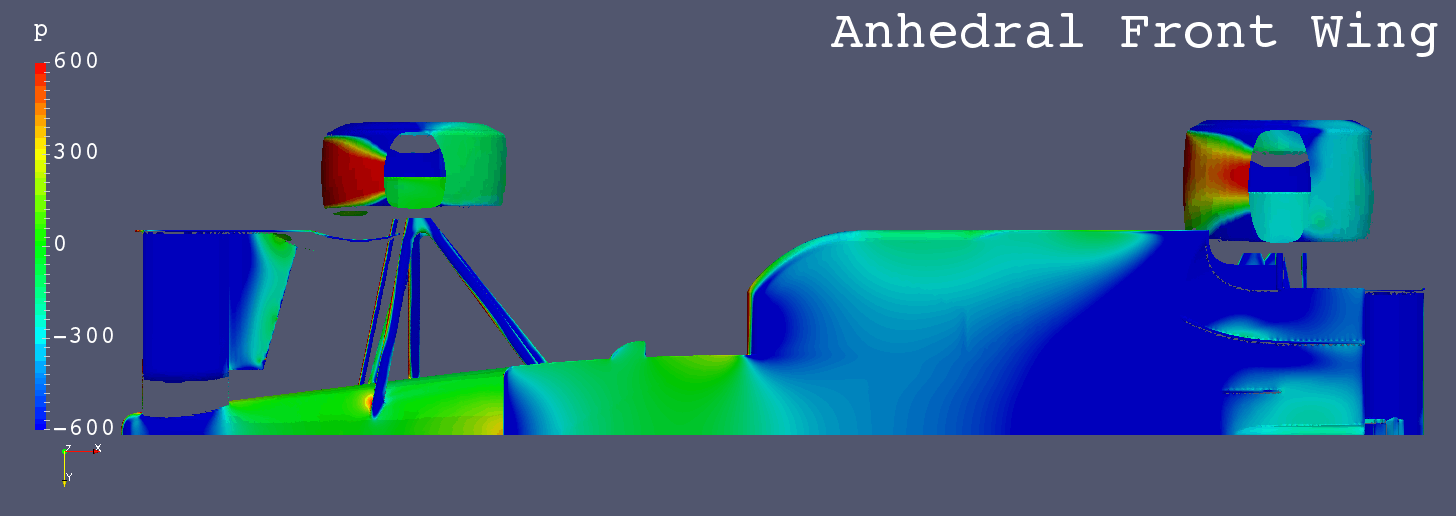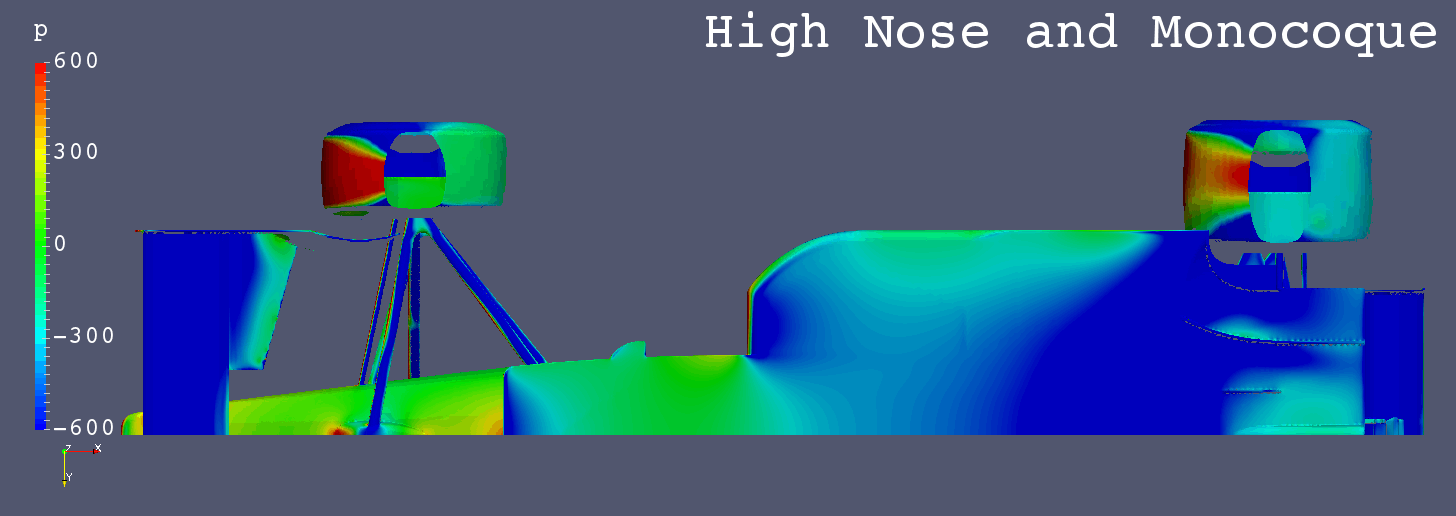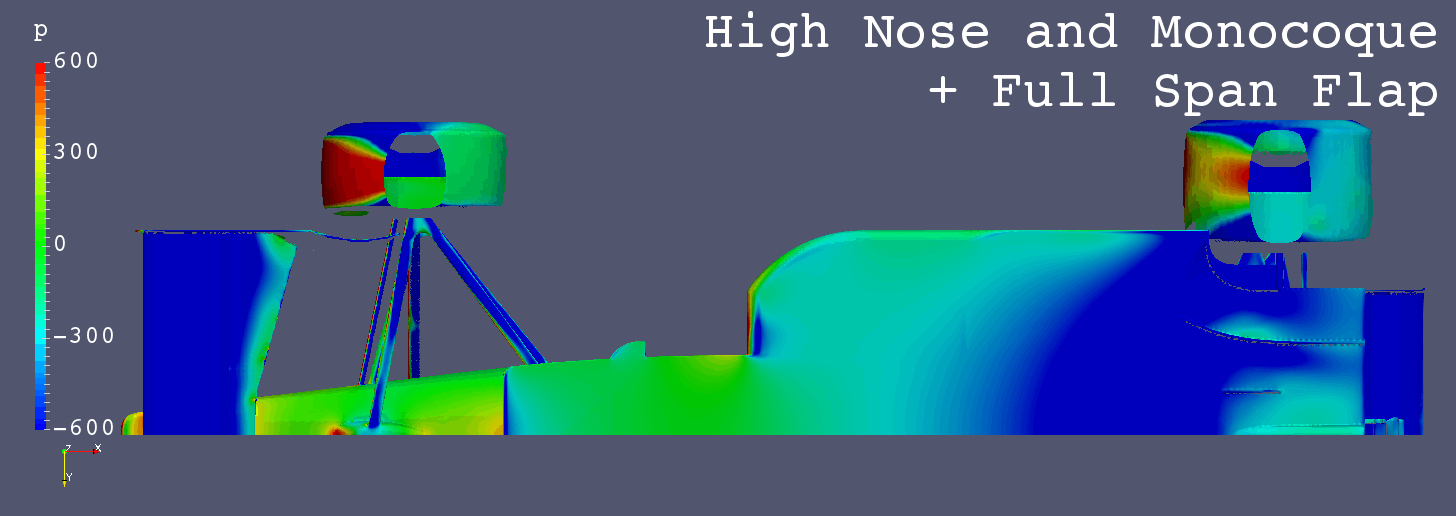
Each Still Images
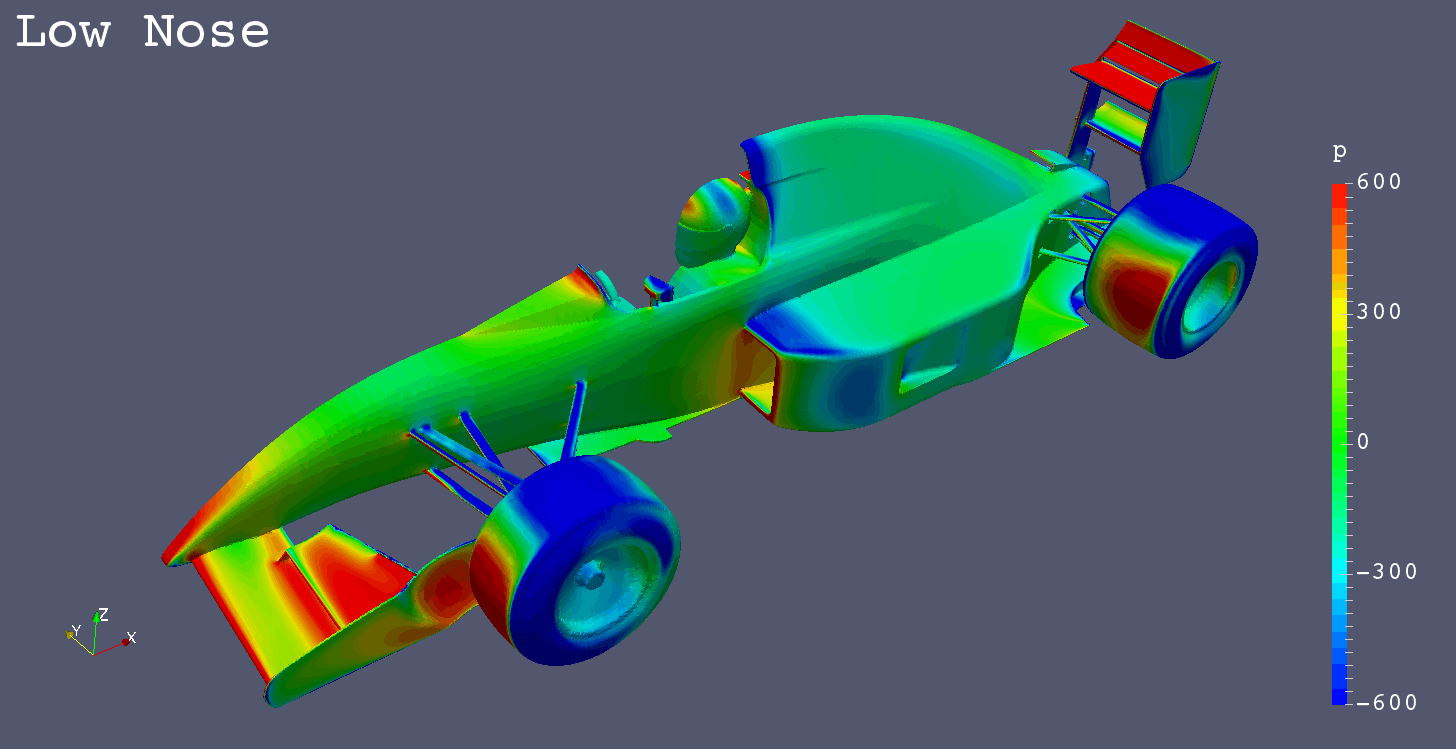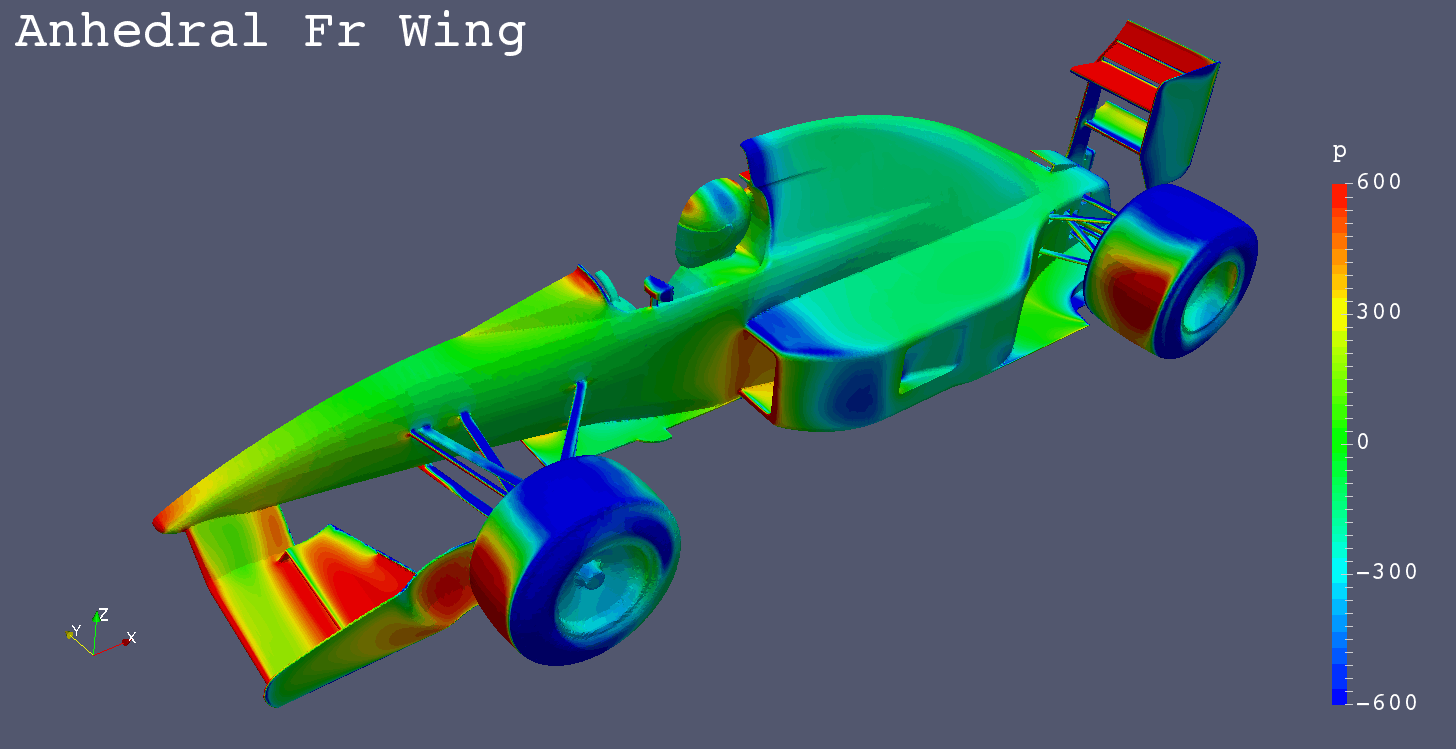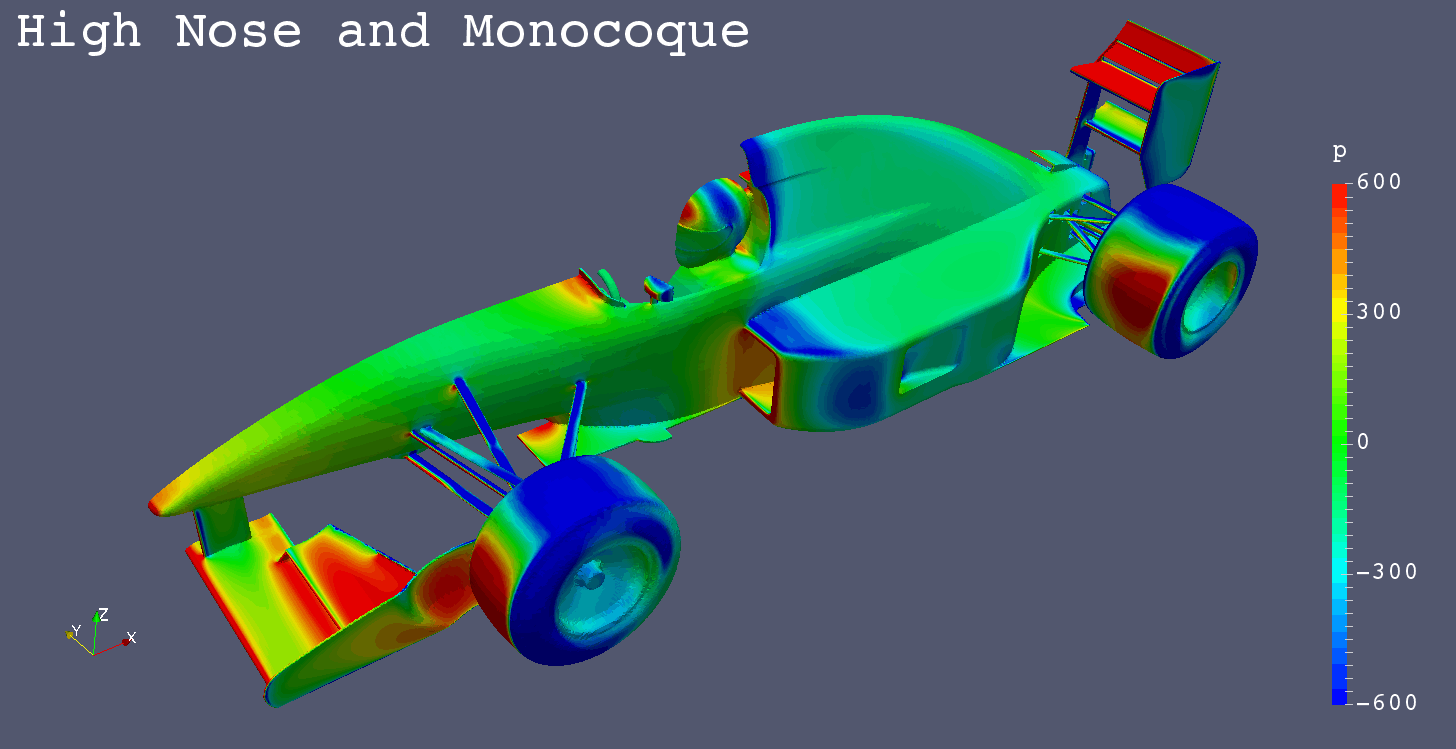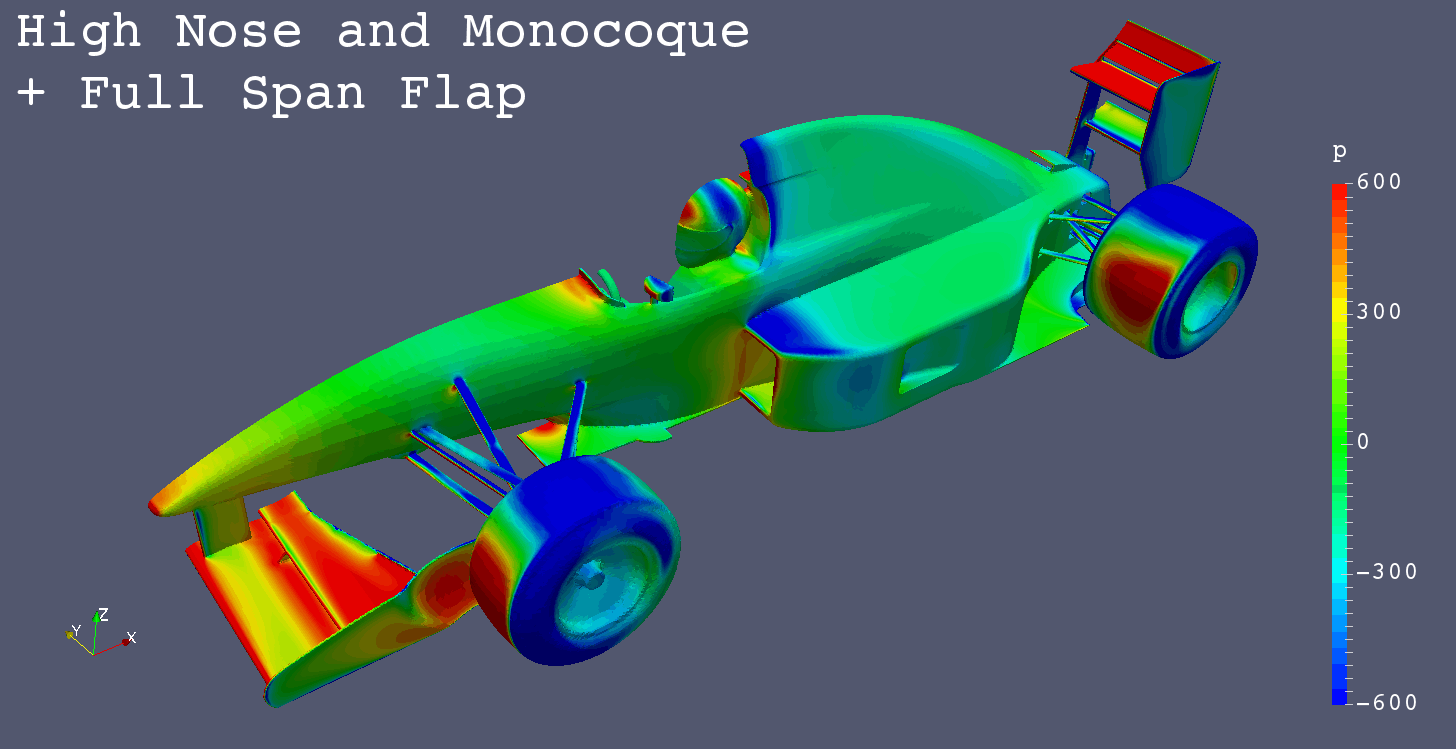
I got a request for “Mono Post Nose” like Footwork Arrows FA12 (1991), so I simulated it additionally.
| Coef. | Whole Car | Body & Wings |
Fr Wing & Nose |
Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cm | 0.3067 | 0.2913 | 0.5464 | -0.4414 | -0.0002 | 0.2385 | 0.4944 | 0.0604 | -0.0450 |
| Cd | 0.9307 | 0.6155 | -0.1173 | 0.0885 | 0.0140 | 0.2770 | 0.2360 | 0.1314 | 0.1838 |
| Cl | -1.7688 | -1.9922 | 0.6510 | -0.5955 | -0.0017 | -0.6952 | -0.6998 | 0.0917 | 0.1317 |
| Clf | -0.5777 | -0.7048 | 0.3295 | -0.7391 | -0.0011 | -0.1091 | 0.1445 | 0.1063 | 0.0208 |
| Clr | -1.1911 | -1.2874 | -0.1581 | 0.1436 | -0.0006 | -0.5861 | -0.8443 | -0.0146 | 0.1109 |
| CoP | 0.6734 | 0.6462 | -0.2428 | -0.2412 | 0.3582 | 0.8431 | 1.2064 | -0.1590 | 0.8420 |
| L/D | -1.9005 | -3.2366 | -5.5483 | -6.7288 | -0.1219 | -2.5097 | -2.9652 | 0.6978 | 0.7166 |
| RF m3/s | 1.0381 |
| Coef. | Low Nose | Anhedral Fr Wing |
Horizontal Fr Wing |
High Monocoque | High Monocoque + Full Span Flap |
Mono Post Nose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.9322 | 0.9291 | 0.9311 | 0.9412 | 0.9476 | 0.9307 |
| Cl | -1.7685 | -1.7557 | -1.7681 | -1.7754 | -1.8414 | -1.7688 |
| Clf | -0.6182 | -0.5216 | -0.5809 | -0.5749 | -0.7764 | -0.5777 |
| Clr | -1.1503 | -1.2341 | -1.1872 | -1.2006 | -1.0650 | -1.1911 |
| CoP | 0.6504 | 0.7029 | 0.6715 | 0.6762 | 0.5783 | 0.6734 |
| L/D | -1.8971 | -1.8896 | -1.8989 | -1.8863 | -1.9431 | -1.9005 |
| RF m3/s | 1.0228 | 1.0411 | 1.0297 | 1.0420 | 0.9741 | 1.0381 |
| Coef. | Low Nose | Anhedral Fr Wing |
Horizontal Fr Wing |
High Monocoque | High Monocoque + Full Span Flap |
Mono Post Nose |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd | 0.0000 | -0.0031 | -0.0011 | 0.0090 | 0.0155 | -0.0015 |
| Cl | 0.0000 | 0.0128 | 0.0004 | -0.0070 | -0.0729 | -0.0003 |
| Clf | 0.0000 | 0.0966 | 0.0373 | 0.0433 | -0.1582 | 0.0405 |
| Clr | 0.0000 | -0.0839 | -0.0369 | -0.0503 | 0.0853 | -0.0408 |
| CoP | 0.0000 | 0.0525 | 0.0210 | 0.0258 | -0.0721 | 0.0230 |
| L/D | 0.0000 | 0.0075 | -0.0017 | 0.0108 | -0.0460 | -0.0034 |
| RF m3/s | 0.0000 | 0.0183 | 0.0069 | 0.0193 | -0.0486 | 0.0153 |
Enlarge the graph of “Mono Post Nose”, “Horizontal Fr Wing” and “High Monocoqe”
| Types | Whole Car | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Nose | -1.7685 | -0.6298 | -0.0234 | -0.6418 | -0.7011 | 0.0928 | 0.1348 |
| Anhedral Fr Wing | -1.7557 | -0.5069 | -0.0386 | -0.7309 | -0.7031 | 0.0917 | 0.1321 |
| Horizontal Fr Wing | -1.7681 | -0.6040 | -0.0023 | -0.6841 | -0.7005 | 0.0918 | 0.1311 |
| High Monocoque | -1.7754 | -0.5981 | 0.0020 | -0.7044 | -0.6998 | 0.0901 | 0.1348 |
| High Monocoque + Full Span Flap | -1.8414 | -0.8181 | 0.0113 | -0.5712 | -0.6912 | 0.0902 | 0.1377 |
| Mono Post Nose | -1.7688 | -0.5955 | -0.0017 | -0.6952 | -0.6998 | 0.0917 | 0.1317 |
| Types | Whole Car | Fr Wing | Nose | Body | Rr Wing | Fr Wheel | Rr Wheel |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low Nose | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Anhedral Fr Wing | 0.0128 | 0.1229 | -0.0152 | -0.0891 | -0.0020 | -0.0011 | -0.0027 |
| Horizontal Fr Wing | 0.0004 | 0.0257 | 0.0211 | -0.0423 | 0.0006 | -0.0010 | -0.0037 |
| High Monocoque | -0.0070 | 0.0316 | 0.0254 | -0.0626 | 0.0013 | -0.0027 | 0.0000 |
| High Monocoque + Full Span Flap | -0.0729 | -0.1883 | 0.0347 | 0.0706 | 0.0099 | -0.0026 | 0.0028 |
| Mono Post Nose | -0.0003 | 0.0343 | 0.0217 | -0.0534 | 0.0013 | -0.0011 | -0.0031 |
Enlarge the graph of “Mono Post Nose”, “Horizontal Fr Wing” and “High Monocoqe”
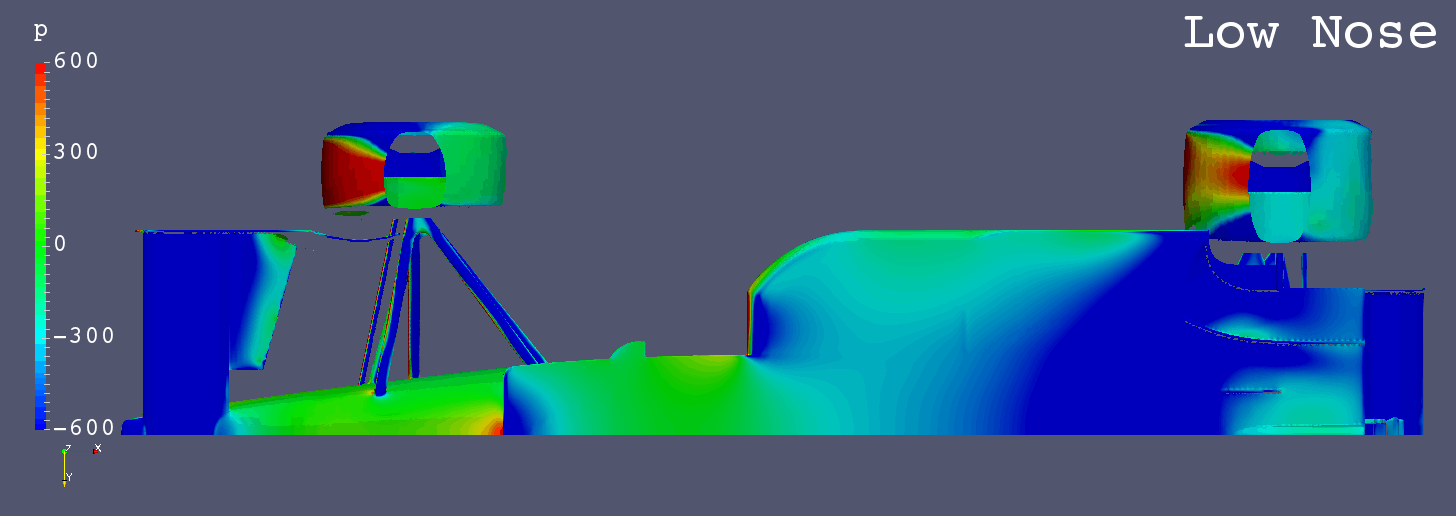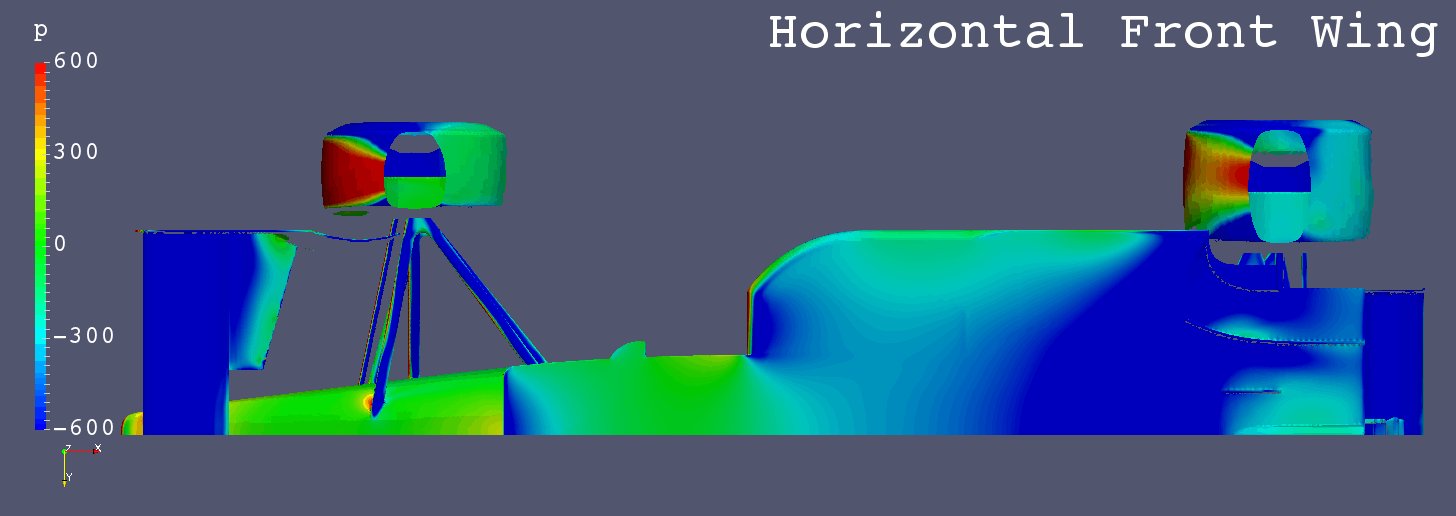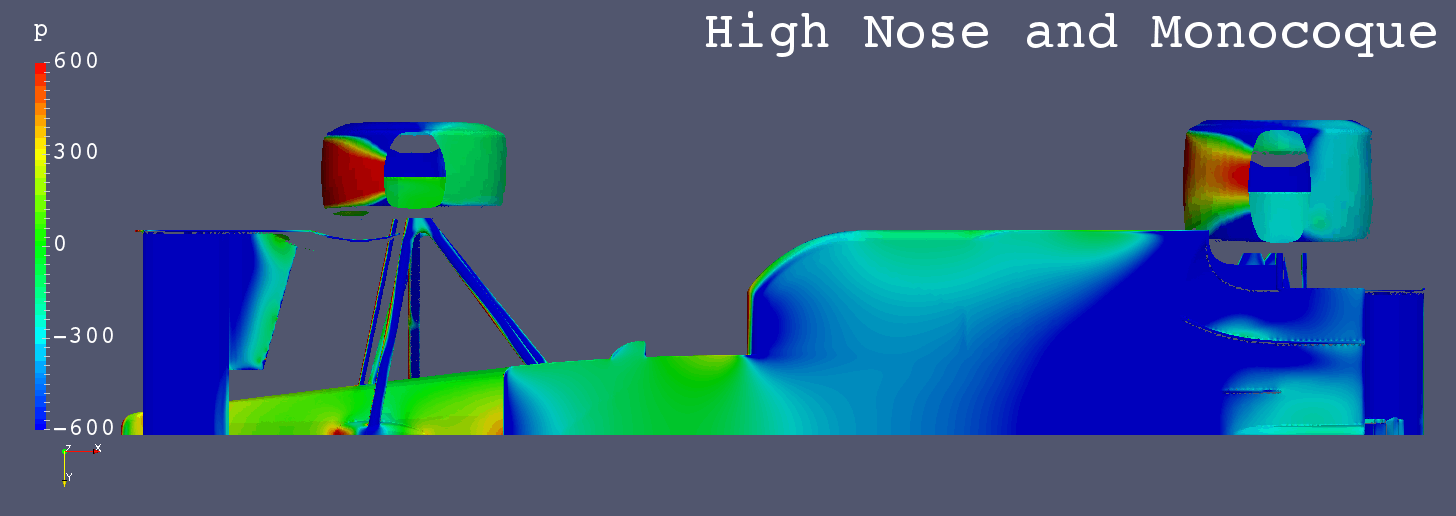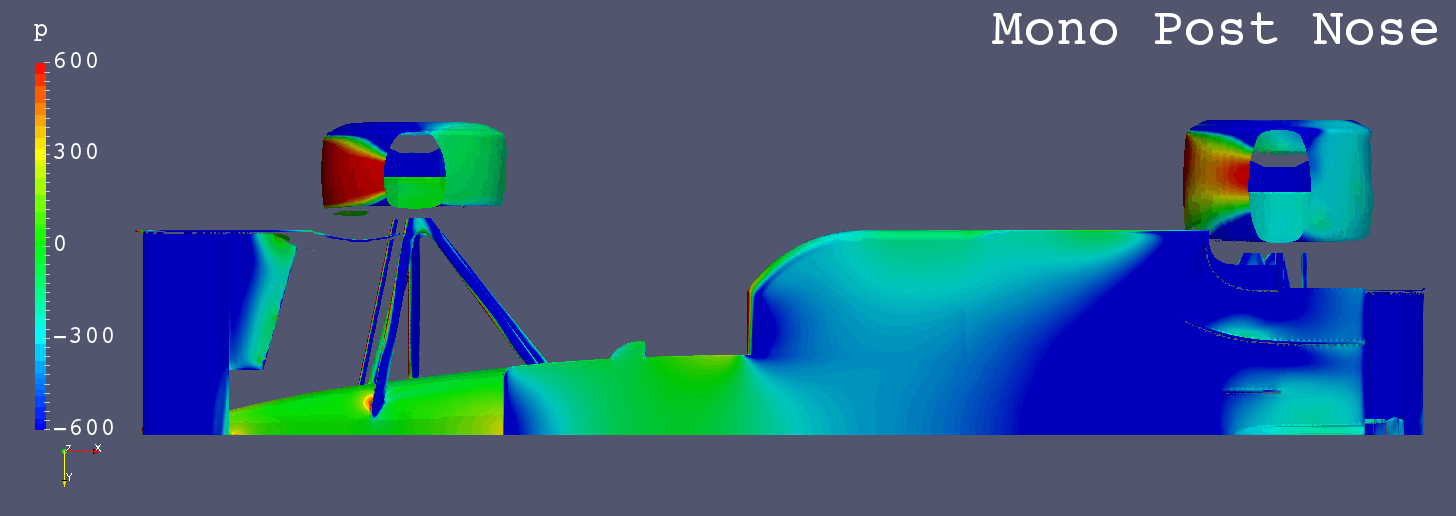
Still Images
Hello. I am working on an assignment called F1 in schools. I need to design a car so I’m researching different features. I am trying to find whether I should use a high or low nose cone. Your article is a bit confusing so I was wondering if you could dumb it down and maybe answer my problem. If you have any further information about F1 cars it would be much appreciated. Thanks!
Hi @yhyams !
Thank you for the reply!
Simpliy put, the final point of the summary is my conclusion.
- It is inferred that the amount of air flow in the area from the nose to the center of the front wing influences the amount of air flow below the floor.
However, whether the high nose or the low nose is optimal depends on the conditions such as vehicle regulations and the engine power.
And there is a further information of my article about an old F1 car - “F92AT - Double Floor”.
Regards,
Yosuke
I’m sorry reliving this old article. I’m new to CFD. My question is: are these coefficients cLA and cDA (area-multiplied) or cL and cD (dimensionless coefficients)?
Thank you.
In this article these are dimensionless quantities (Cl, Cd).
Thanks!
Thank you for your reply yosukegb4!
Do you happen to have or remember the forces values or the areas?
Cheers
The reference area value is 0.73288 m^2. @stormrider96150
I did not evaluate the force values in absolute terms. Because that would require comparison with wind tunnel tests and actual vehicle tests, which was not possible.
So I made relative evaluations by comparing the differences in calculation results due to differences in shape.
Regards,
Yosuke